Project 4: Ghostscript Source Code Exploration Tool
Project Overview
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Level 3: Advanced |
| Time Estimate | 2-3 weeks |
| Programming Language | C (reading), Python/Rust (tooling) |
| Knowledge Area | Document Processing / Code Analysis |
| Prerequisites | Understanding from Projects 1-3 |
What you’ll build: An annotated walkthrough/visualization of Ghostscript’s actual conversion pipeline, with instrumentation to trace PS execution through PDF output.
Why it matters: Ghostscript is the production implementation that powers PDF generation worldwide. Understanding its architecture shows you how professionals solved these problems at scale, and gives you insight into real-world systems programming.
Learning Objectives
By completing this project, you will:
- Navigate a large C codebase (~1M lines of code)
- Understand the device abstraction layer that enables multiple output formats
- Trace execution flow from PostScript input to PDF output
- Document key data structures and their roles
- Add instrumentation to observe the conversion process
- Learn techniques for understanding legacy code
The Core Question You’re Answering
“How does Ghostscript actually work? What happens inside when you run
gs -sDEVICE=pdfwrite?”
This project takes you from “I can use Ghostscript” to “I understand how Ghostscript works internally.” You’ll:
- Map the architecture through code exploration
- Identify the key modules and their responsibilities
- Trace the data flow from input to output
- Document the design decisions and patterns used
Deep Theoretical Foundation
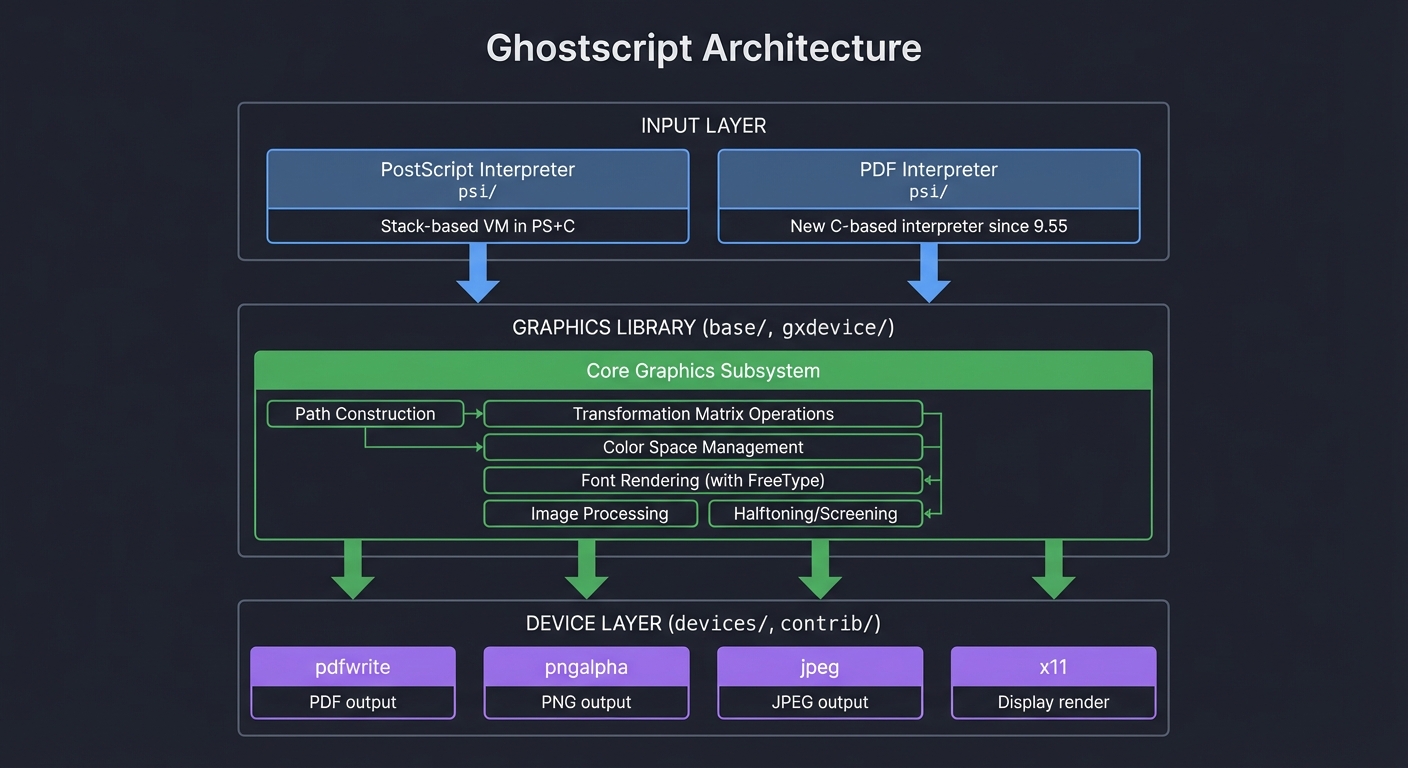
1. Ghostscript Architecture Overview
Ghostscript is organized into layers:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ GHOSTSCRIPT ARCHITECTURE │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ INPUT LAYER │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ PostScript │ │ PDF Interpreter │ │ │
│ │ │ Interpreter │ │ (psi/) │ │ │
│ │ │ (psi/) │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ New C-based │ │ │
│ │ │ Stack-based VM │ │ interpreter │ │ │
│ │ │ implemented in │ │ (since 9.55) │ │ │
│ │ │ PS + C │ │ │ │ │
│ │ └──────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘ │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ GRAPHICS LIBRARY │ │
│ │ (base/, gxdevice/) │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Core Graphics Subsystem │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ • Path construction and manipulation │ │ │
│ │ │ • Transformation matrix operations │ │ │
│ │ │ • Color space management │ │ │
│ │ │ • Font rendering (FreeType integration) │ │ │
│ │ │ • Image processing │ │ │
│ │ │ • Halftoning and screening │ │ │
│ │ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ DEVICE LAYER │ │
│ │ (devices/, contrib/) │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ┌────────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌────────┐ │ │
│ │ │pdfwrite│ │pngalpha│ │ jpeg │ │ x11 │ ... │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ PDF │ │ PNG │ │ JPEG │ │Display │ │ │
│ │ │ output │ │ output │ │ output │ │ render │ │ │
│ │ └────────┘ └────────┘ └────────┘ └────────┘ │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
2. Key Directory Structure
ghostscript/
├── base/ # Core graphics library
│ ├── gx*.c # Graphics primitives
│ ├── gs*.c # State management
│ └── gp*.c # Platform-specific code
├── psi/ # PostScript interpreter
│ ├── i*.c # Interpreter core
│ ├── z*.c # Operator implementations
│ └── int*.c # Interpreter utilities
├── devices/ # Output devices
│ ├── vector/ # Vector devices (PDF, PS, etc.)
│ │ ├── gdevpdf*.c # PDF writer device
│ │ └── gdevpsdf.c # Common PS/PDF code
│ └── gdev*.c # Raster devices (PNG, JPEG, etc.)
├── lib/ # PostScript library files (.ps)
├── Resource/ # Fonts, ICC profiles, etc.
└── doc/ # Documentation
3. The Device Interface
The genius of Ghostscript is the device abstraction. Every output format implements the same interface:
// Simplified device structure (actual is much larger)
typedef struct gx_device_s {
/* Device identification */
const char *dname; // Device name
int width, height; // Page dimensions
float HWResolution[2]; // Resolution
/* Device procedures */
gx_device_procs procs; // Function pointers
} gx_device;
// Device procedure structure
typedef struct gx_device_procs_s {
/* Initialization */
dev_proc_open_device((*open_device));
dev_proc_close_device((*close_device));
/* Drawing operations */
dev_proc_fill_rectangle((*fill_rectangle));
dev_proc_fill_path((*fill_path));
dev_proc_stroke_path((*stroke_path));
dev_proc_fill_mask((*fill_mask));
/* Text operations */
dev_proc_text_begin((*text_begin));
/* Image operations */
dev_proc_begin_image((*begin_image));
dev_proc_image_data((*image_data));
dev_proc_end_image((*end_image));
/* Page control */
dev_proc_output_page((*output_page));
/* And many more... */
} gx_device_procs;
4. The pdfwrite Device
The pdfwrite device is what creates PDF output. Key files:
devices/vector/gdevpdfb.c- PDF bitmap outputdevices/vector/gdevpdfc.c- PDF color handlingdevices/vector/gdevpdfd.c- PDF drawing operationsdevices/vector/gdevpdfe.c- PDF encryptiondevices/vector/gdevpdff.c- PDF fontsdevices/vector/gdevpdfg.c- PDF graphics statedevices/vector/gdevpdfm.c- PDF metadatadevices/vector/gdevpdfo.c- PDF objectsdevices/vector/gdevpdfp.c- PDF pagesdevices/vector/gdevpdft.c- PDF textdevices/vector/gdevpdfx.c- PDF/X support
Project Specification
Phase 1: Build and Explore (Days 1-3)
- Build Ghostscript from source
- Clone the repository
- Configure and build with debug symbols
- Run basic tests
- Explore the codebase
- Generate tags (ctags/cscope)
- Create a map of key files and functions
- Document the main entry points
Phase 2: Trace the Pipeline (Days 4-7)
- Instrument the interpreter
- Add logging to key functions
- Trace operator execution
- Watch stack operations
- Instrument the graphics library
- Log path construction
- Log color changes
- Track transformation matrix changes
- Instrument the pdfwrite device
- Log PDF object creation
- Track content stream generation
- Watch xref table building
Phase 3: Document and Visualize (Days 8-14)
- Create architecture documentation
- Draw component diagrams
- Document key data structures
- Explain the data flow
- Build visualization tools
- Parse trace logs
- Generate sequence diagrams
- Create call graphs
- Write the exploration guide
- Document your exploration process
- Explain key discoveries
- Provide guidance for others
Solution Architecture
Exploration Tools
You’ll build tools to understand the codebase:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ EXPLORATION TOOLKIT │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ BUILD & INSTRUMENT │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ./configure --enable-debug │ │
│ │ make CFLAGS="-g -O0 -DTRACE_ENABLED" │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ CODE NAVIGATION │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ctags -R . # Generate tags │ │
│ │ cscope -bqR # Build cscope database │ │
│ │ grep -rn "gx_device_procs" # Find device interface │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ TRACING │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ GDB scripts to set breakpoints │ │
│ │ printf-style logging in key functions │ │
│ │ Stack trace capture at critical points │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ VISUALIZATION │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ Python scripts to parse logs │ │
│ │ Generate Mermaid/PlantUML diagrams │ │
│ │ Create HTML exploration guide │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘

Implementation Guide
Phase 1: Building Ghostscript
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/ArtifexSoftware/ghostpdl.git
cd ghostpdl
# Install dependencies (Ubuntu/Debian)
sudo apt-get install build-essential libfreetype6-dev libpng-dev \
libjpeg-dev libtiff-dev libopenjp2-7-dev zlib1g-dev
# Configure with debug symbols
./autogen.sh --prefix=/usr/local --enable-debug
# Build with tracing enabled
make CFLAGS="-g -O0 -DDEBUG"
# Test the build
./bin/gs -h
# Run a simple conversion
./bin/gs -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -o test.pdf test.ps
Phase 2: Code Navigation Setup
# Generate ctags
ctags -R --languages=C --exclude=obj --exclude=bin .
# Generate cscope database
find . -name "*.c" -o -name "*.h" | cscope -bqR -i -
# Use with vim/nvim
vim -t gx_device_procs
# Or use vscode with C/C++ extension
Phase 3: Key Functions to Trace
Create a GDB script to trace key functions:
# trace_gs.gdb - GDB script for Ghostscript exploration
# Break at interpreter main loop
break zpush
commands
printf "PUSH: %p\n", $rdi
continue
end
# Break at path operations
break gx_path_add_line
commands
printf "LINE: (%.2f, %.2f)\n", *(double*)($rdi+8), *(double*)($rdi+16)
continue
end
# Break at PDF object creation
break cos_object_alloc
commands
printf "PDF_OBJ: type=%d\n", $rsi
continue
end
# Break at page output
break pdf_output_page
commands
printf "PAGE: %d\n", $rsi
continue
end
# Run with a test file
run -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -o out.pdf test.ps
Phase 4: Add Printf Tracing
Add trace macros to key files:
// Add to base/gxpath.c
#ifdef TRACE_ENABLED
#define TRACE_PATH(fmt, ...) \
fprintf(stderr, "[PATH] " fmt "\n", ##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define TRACE_PATH(fmt, ...)
#endif
int
gx_path_add_line(gx_path *ppath, fixed x, fixed y)
{
TRACE_PATH("add_line: (%.2f, %.2f)",
fixed2float(x), fixed2float(y));
// Original implementation...
}
int
gx_path_add_curve(gx_path *ppath,
fixed x1, fixed y1, fixed x2, fixed y2, fixed x3, fixed y3)
{
TRACE_PATH("add_curve: (%.2f,%.2f) (%.2f,%.2f) (%.2f,%.2f)",
fixed2float(x1), fixed2float(y1),
fixed2float(x2), fixed2float(y2),
fixed2float(x3), fixed2float(y3));
// Original implementation...
}
Phase 5: Trace Log Parser
Create a Python script to parse and visualize traces:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""Parse Ghostscript trace logs and generate visualizations."""
import re
import sys
from collections import defaultdict
def parse_trace_log(filename):
"""Parse a trace log file into structured events."""
events = []
patterns = {
'path': re.compile(r'\[PATH\] (\w+): (.*)'),
'stack': re.compile(r'\[STACK\] (\w+): (.*)'),
'pdf': re.compile(r'\[PDF\] (\w+): (.*)'),
'page': re.compile(r'\[PAGE\] (\w+): (.*)'),
}
with open(filename) as f:
for line_num, line in enumerate(f, 1):
for category, pattern in patterns.items():
match = pattern.match(line)
if match:
events.append({
'line': line_num,
'category': category,
'operation': match.group(1),
'data': match.group(2),
})
break
return events
def generate_sequence_diagram(events):
"""Generate a Mermaid sequence diagram from events."""
print("sequenceDiagram")
print(" participant PS as PostScript")
print(" participant GFX as Graphics")
print(" participant PDF as pdfwrite")
for event in events[:50]: # Limit for readability
if event['category'] == 'stack':
print(f" PS->>GFX: {event['operation']}")
elif event['category'] == 'path':
print(f" GFX->>GFX: {event['operation']}")
elif event['category'] == 'pdf':
print(f" GFX->>PDF: {event['operation']}")
def generate_stats(events):
"""Generate statistics from events."""
by_category = defaultdict(int)
by_operation = defaultdict(int)
for event in events:
by_category[event['category']] += 1
by_operation[event['operation']] += 1
print("\n=== Event Statistics ===\n")
print("By Category:")
for cat, count in sorted(by_category.items()):
print(f" {cat}: {count}")
print("\nTop 20 Operations:")
for op, count in sorted(by_operation.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:20]:
print(f" {op}: {count}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: parse_trace.py <trace_log>")
sys.exit(1)
events = parse_trace_log(sys.argv[1])
generate_stats(events)
if '--diagram' in sys.argv:
generate_sequence_diagram(events)
Phase 6: Document Key Discoveries
Create a markdown exploration guide:
# Ghostscript Exploration Guide
## Entry Points
### Main Entry: `gs_main()`
Location: `psi/gs.c`
This is where everything starts. Key initialization:
1. `gs_main_init()` - Initialize interpreter state
2. `gs_main_add_lib_path()` - Set up library paths
3. `gs_main_run_string()` - Execute PostScript
### Operator Execution
Location: `psi/interp.c`
The `gs_call_operator()` function dispatches to operator implementations.
Operators are implemented in `psi/z*.c` files:
- `zpush.c` - Stack operations
- `zpaint.c` - Painting operators (stroke, fill)
- `zpath.c` - Path construction
## Data Flow
PostScript Input ↓ Tokenizer (psi/iscan.c) ↓ Interpreter (psi/interp.c) ↓ Operator dispatch (psi/zfont.c, zpaint.c, etc.) ↓ Graphics library (base/gx.c) ↓ Device interface (gxdevice.h) ↓ pdfwrite device (devices/vector/gdevpdf.c) ↓ PDF Output
## Key Data Structures
### gx_path (base/gxpath.h)
Represents a graphics path. Contains:
- `segments` - List of path segments (move, line, curve)
- `bbox` - Bounding box
- `state` - Current position
### gs_gstate (base/gxistate.h)
The graphics state. Contains:
- `ctm` - Current transformation matrix
- `color` - Current color
- `line_params` - Line width, cap, join
- `font` - Current font
### gx_device (base/gxdevice.h)
Abstract device interface. Key methods:
- `fill_path()` - Fill a path
- `stroke_path()` - Stroke a path
- `output_page()` - End of page
### pdf_device (devices/vector/gdevpdfx.h)
PDF-specific device state:
- `objects` - PDF object array
- `pages` - Page objects
- `streams` - Content streams
Testing and Validation
Trace a Simple Conversion
# Create test file
cat > test_simple.ps << 'EOF'
%!PS-Adobe-3.0
100 100 moveto
200 200 lineto
stroke
showpage
EOF
# Run with tracing
./bin/gs -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -o test.pdf test_simple.ps 2>&1 | tee trace.log
# Parse the trace
python3 parse_trace.py trace.log
Verify Understanding
- Can you explain the path from
movetoto PDFmoperator?- PostScript
moveto→zpaint.c:zmoveto() - →
gx_path_add_point()in graphics library - → pdfwrite captures path
- → Outputs
100 100 min content stream
- PostScript
- Can you trace a color change?
- PostScript
setgray→zcolor.c:zsetgray() - → Updates
gs_gstate.color - → pdfwrite outputs
0.5 g 0.5 G
- PostScript
- Can you trace a page boundary?
- PostScript
showpage→zdevice.c:zshowpage() - →
gx_output_page()in graphics library - →
pdf_output_page()in pdfwrite device - → Finalizes page object, starts new one
- PostScript
Common Pitfalls
1. Build Issues
Ghostscript has many dependencies. Common fixes:
# Missing FreeType
sudo apt-get install libfreetype6-dev
# Missing libjpeg
sudo apt-get install libjpeg-dev
# Build with specific features disabled
./configure --disable-cups --disable-gtk
2. Debug Build Performance
Debug builds are much slower. For tracing, consider:
# Selective optimization
make CFLAGS="-g -O0" base/gxpath.o # Debug this file
make CFLAGS="-g -O2" # Optimize others
3. Code Complexity
Ghostscript is complex. Focus on:
- The device interface (
gxdevice.h) - One device implementation (
gdevpdf*.c) - One operator path (
zpath.c→gxpath.c)
Don’t try to understand everything at once.
Extensions
Level 1: Create a Call Graph
Use cflow or calltree to generate function call graphs.
Level 2: Compare Devices
Trace the same PS file through pdfwrite and pngalpha. Document the differences.
Level 3: Profile Performance
Use perf to identify hot spots in the conversion pipeline.
Level 4: Contribute a Fix
Find a bug or improvement and submit a patch to the Ghostscript project.
Self-Assessment
Before considering this project complete:
- Can build Ghostscript from source with debug symbols
- Can navigate the codebase using ctags/cscope
- Can trace a simple PS-to-PDF conversion through the code
- Have documented the key components and data flow
- Can explain the device abstraction layer
- Have created visualization tools for trace data
Resources
Essential Reading
- Working Effectively with Legacy Code by Michael Feathers
- 21st Century C by Ben Klemens (for C patterns)
- Ghostscript documentation: https://ghostscript.readthedocs.io/
Tools
- GDB: GNU Debugger
- Valgrind: Memory analysis
- perf: Performance profiling
- cflow/calltree: Call graph generation
- ctags/cscope: Code navigation
Community
- Ghostscript mailing lists
- GitHub issues: https://github.com/ArtifexSoftware/ghostpdl