Final Project: DevOps Automation Platform
Integrate every previous project into a unified, modular automation platform.
Quick Reference
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Level 5: Master |
| Time Estimate | 2-3 months |
| Language | Bash (Alternatives: Python, Go) |
| Prerequisites | Projects 1-15 complete, strong systems knowledge |
| Key Topics | modular architecture, orchestration, state management, observability |
1. Learning Objectives
By completing this project, you will:
- Design a modular CLI platform with pluggable modules.
- Integrate backup, deployment, monitoring, and security workflows.
- Implement a shared configuration and state system.
- Build consistent logging, error handling, and reporting.
- Deliver end-to-end workflows like “deploy with backup and tests.”
2. Theoretical Foundation
2.1 Core Concepts
- Modular architecture: Separating concerns into reusable modules.
- Shared services: Logging, config, state, and events.
- Workflow orchestration: Sequencing and rollback logic.
- Observability: Unified metrics and logs.
- Failure domains: Isolating failures across modules.
2.2 Why This Matters
This is how real DevOps platforms work: integrate tools into one cohesive system with consistent UX and reliable state handling.
2.3 Historical Context / Background
Platforms like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, and internal DevOps CLIs evolved from small scripts into unified toolchains. This project mirrors that evolution.
2.4 Common Misconceptions
- “Integration is just calling scripts.” It’s also about shared state and error handling.
- “More features = better platform.” Consistency and reliability matter most.
3. Project Specification
3.1 What You Will Build
A devops CLI that loads modules dynamically (backup, deploy, monitor, security, tasks), provides unified config and logging, and supports integrated workflows.
3.2 Functional Requirements
- Module loader: Discover and load modules automatically.
- Shared config: Centralized config with overrides.
- Shared logging: Unified logging levels and formats.
- Workflow engine: Run multi-step workflows with rollback.
- Event system: Basic pub/sub for module communication.
- Command routing:
devops <module> <command>.
3.3 Non-Functional Requirements
- Reliability: Failures propagate clearly with rollback.
- Extensibility: Add modules with minimal boilerplate.
- Usability: Consistent help text and flags across modules.
3.4 Example Usage / Output
$ devops deploy production --backup-first --run-tests --notify
[devops] backup: completed (id=20241231_120000)
[devops] tests: 124 passed
[devops] deploy: release 20241231_120500 live
[devops] notify: slack message sent
3.5 Real World Outcome
You have a functioning DevOps platform that combines deployment, monitoring, backup, and audit into one CLI, suitable for real teams.
4. Solution Architecture
4.1 High-Level Design
cli -> router -> modules -> shared services
| |
| +-> config, logging, state
+-> workflows & events
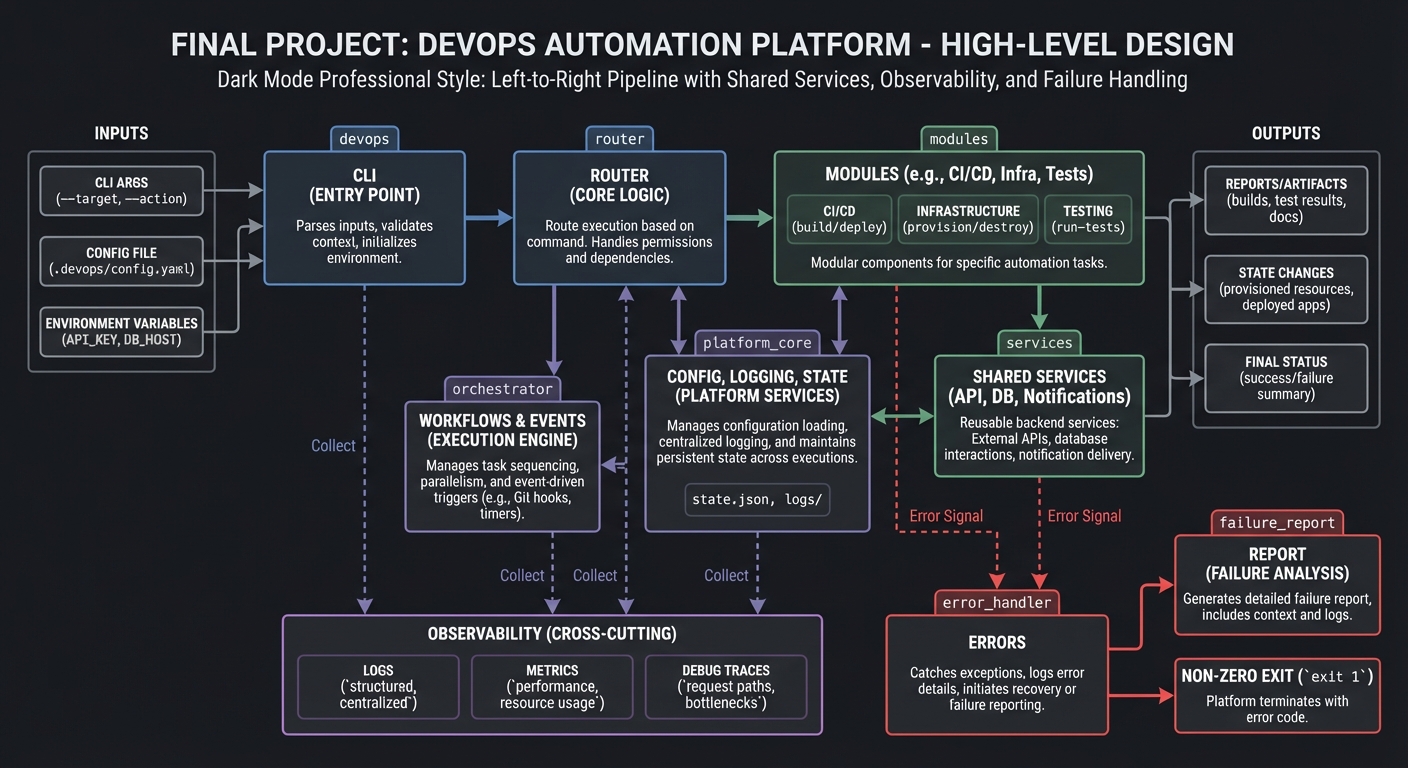
4.2 Key Components
| Component | Responsibility | Key Decisions |
|---|---|---|
| Module loader | Discover and register modules | filesystem convention |
| Router | Map commands to modules | command table |
| State store | Persist workflow state | JSON + locking |
| Event bus | Publish/subscribe | file-based queue |
| Logger | Consistent logging | levels + timestamps |
4.3 Data Structures
state/
workflows.json
last_run.json
logs/
devops.log
4.4 Algorithm Overview
Key Algorithm: Workflow Execution
- Load workflow definition.
- Execute steps sequentially.
- On failure, run rollback steps.
- Emit events and log results.
Complexity Analysis:
- Time: O(steps) per workflow
- Space: O(state size)
5. Implementation Guide
5.1 Development Environment Setup
sudo apt-get install jq
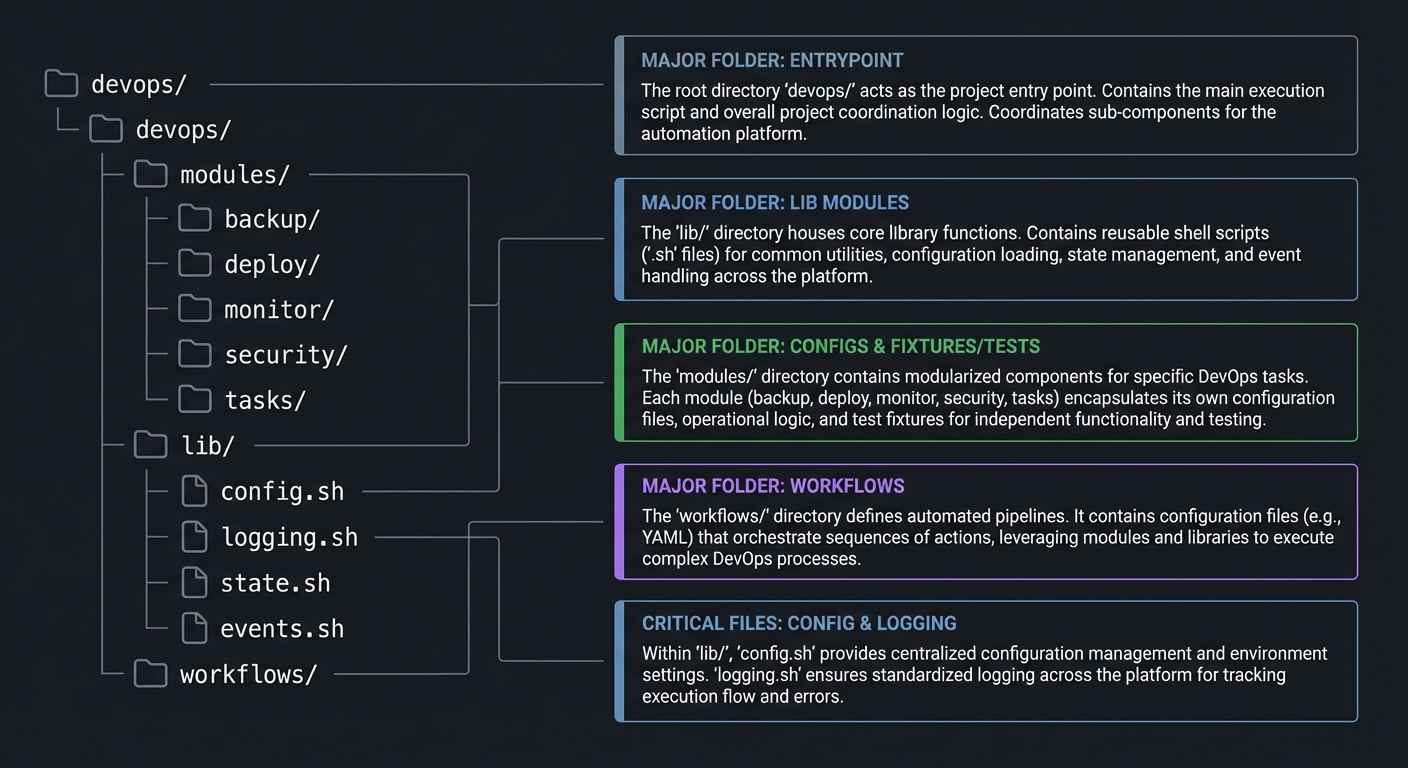
5.2 Project Structure
devops/
|-- devops
|-- modules/
| |-- backup/
| |-- deploy/
| |-- monitor/
| |-- security/
| `-- tasks/
|-- lib/
| |-- config.sh
| |-- logging.sh
| |-- state.sh
| `-- events.sh
`-- workflows/
5.3 The Core Question You Are Answering
“How do I orchestrate many reliable tools into one cohesive platform?”
5.4 Concepts You Must Understand First
- Module boundaries and interfaces
- Shared state and locking
- Error propagation and rollback
5.5 Questions to Guide Your Design
- How do modules declare their commands and help text?
- How does the router resolve conflicts between module commands?
- Where should shared configuration live?
5.6 Thinking Exercise
Design a workflow graph for “deploy with backup and tests.” Identify rollback points.
5.7 The Interview Questions They Will Ask
- How do you ensure new modules don’t break old ones?
- How does your system recover from partial failures?
- How do you manage shared state safely?
5.8 Hints in Layers
Hint 1: Start with a module loader that sources modules/*/module.sh.
Hint 2: Build a router that maps devops backup to module functions.
Hint 3: Add shared config and logging before workflows.
Hint 4: Add workflows and rollback logic last.
5.9 Books That Will Help
| Topic | Book | Chapter |
|---|---|---|
| DevOps practices | “The DevOps Handbook” | Part II |
| System integration | “The Phoenix Project” | Entire book |
5.10 Implementation Phases
Phase 1: Core Platform (2-3 weeks)
Goals:
- Module loader, router, shared config.
Tasks:
- Build module discovery.
- Implement config and logging.
Checkpoint: Modules load and commands route correctly.
Phase 2: Workflow Integration (3-4 weeks)
Goals:
- Run multi-step workflows.
Tasks:
- Add workflow definitions.
- Implement rollback hooks.
Checkpoint: Workflow executes end-to-end.
Phase 3: Polish and Extensibility (2-3 weeks)
Goals:
- Documentation and module templates.
Tasks:
- Add module scaffolding generator.
- Improve reporting and status.
Checkpoint: New module can be added in under 30 minutes.
5.11 Key Implementation Decisions
| Decision | Options | Recommendation | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Module API | functions vs scripts | functions | shared state |
| State store | JSON vs sqlite | JSON | simpler |
| Event system | file-based vs in-memory | file-based | durability |
6. Testing Strategy
6.1 Test Categories
| Category | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Unit | module APIs | loader tests |
| Integration | workflows | deploy with backup |
| End-to-end | full CLI | real command runs |
6.2 Critical Test Cases
- Workflow rollback triggered on failure.
- Module registration handles duplicates.
- Config overrides apply correctly.
6.3 Test Data
fixtures/workflow_deploy.json
7. Common Pitfalls and Debugging
7.1 Frequent Mistakes
| Pitfall | Symptom | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No rollback | partial failures | implement rollback steps |
| Global state conflicts | inconsistent behavior | centralize state access |
| Inconsistent CLI UX | confusion | shared help generator |
7.2 Debugging Strategies
- Trace workflow execution with debug logs.
- Validate module contracts on load.
7.3 Performance Traps
Over-logging can slow workflows. Make verbosity configurable.
8. Extensions and Challenges
8.1 Beginner Extensions
- Add
devops doctorhealth check. - Add module documentation generator.
8.2 Intermediate Extensions
- Add remote execution support.
- Add plugin marketplace layout.
8.3 Advanced Extensions
- Add web dashboard for workflows.
- Add distributed execution.
9. Real-World Connections
9.1 Industry Applications
- Internal DevOps CLIs.
- Release pipelines for production systems.
9.2 Related Open Source Projects
- fabric: remote execution toolkit.
- ansible: declarative automation.
9.3 Interview Relevance
- Demonstrates system design and integration skills.
- Shows ability to build scalable automation platforms.
10. Resources
10.1 Essential Reading
- “The DevOps Handbook”
- “The Phoenix Project”
10.2 Video Resources
- “DevOps Toolchains” (YouTube)
10.3 Tools and Documentation
jq,rsync,ssh,shellcheck
10.4 Related Projects in This Series
- Projects 1-15 (all modules)
11. Self-Assessment Checklist
11.1 Understanding
- I can explain module boundaries and shared services.
- I can describe rollback strategies.
11.2 Implementation
- Workflows run end-to-end.
- Errors propagate with clear messages.
11.3 Growth
- I can add new modules quickly.
12. Submission / Completion Criteria
Minimum Viable Completion:
- Module loader + command routing
Full Completion:
- Integrated workflows with rollback
Excellence (Going Above & Beyond):
- Distributed execution + dashboard