Project 5: Autonomous Research Agent with Memory
Build an AI agent that autonomously researches topics, builds a knowledge graph of discovered facts, and synthesizes comprehensive reports with citations.
Quick Reference
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Advanced (Level 3) |
| Time Estimate | 2-3 weeks |
| Language | TypeScript (Alternatives: Python, Go, JavaScript) |
| Prerequisites | Completed Projects 1-4, familiarity with async/await, basic graph concepts |
| Key Topics | Multi-tool agents, knowledge graphs, autonomous decision-making, state management |
| AI SDK Concepts | agent(), prepareStep, stopWhen, multi-tool orchestration |
1. Learning Objectives
By completing this project, you will:
- Master multi-tool agent orchestration: Design and implement agents that coordinate multiple tools (search, read, extract, store, query) to accomplish complex goals
- Implement stateful agent loops: Maintain and evolve agent state (knowledge graph) across many iterations using
prepareStepfor context injection - Design intelligent termination conditions: Use
stopWhento create agents that autonomously decide when they have gathered sufficient information - Build in-memory knowledge graphs: Represent discovered facts as nodes (entities) and edges (relationships) with confidence scores
- Apply the ReAct pattern: Implement the Reasoning-Acting loop that underlies modern AI agents
- Create structured outputs with citations: Use
generateObjectto produce well-formed research reports with proper source attribution - Handle real-world API integration: Work with web search and page fetching in production-quality agent systems
2. Deep Theoretical Foundation
2.1 Multi-Tool Agent Orchestration
Modern AI agents are not single-purpose tools. They coordinate multiple capabilities to achieve complex goals. This orchestration is the fundamental pattern that separates simple LLM wrappers from true agent systems.
THE TOOL ORCHESTRATION PATTERN
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ AGENT CORE │
│ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ LLM (The Brain) │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ "Given my current knowledge and the user's question, │ │
│ │ what tool should I use next?" │ │
│ └─────────────────────────┬────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌──────────────┼──────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ │
│ │ webSearch │ │ readPage │ │extractFacts │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ Find URLs │ │ Get content │ │ Parse into │ │
│ │ for a query │ │ from a URL │ │ structured │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ facts │ │
│ └──────┬──────┘ └──────┬──────┘ └──────┬──────┘ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ ┌──────────┼────────────────┘ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ │
│ │ addToGraph │ │ queryGraph │ │synthesize │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │Report │ │
│ │ Store facts │ │ Search own │ │ │ │
│ │ in memory │ │ memory │ │ Final output│ │
│ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ │
│ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
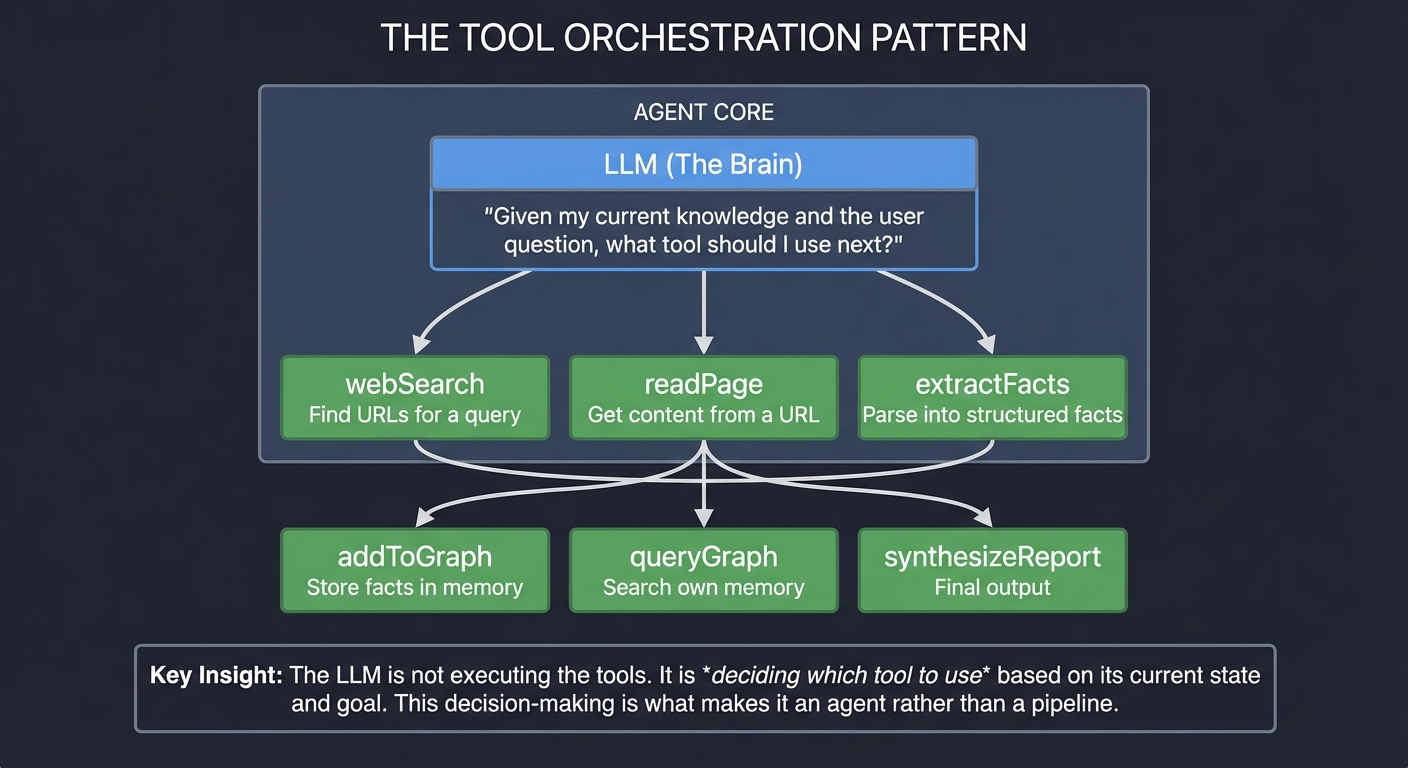
Key Insight: The LLM is not executing the tools. It is deciding which tool to use based on its current state and goal. This decision-making is what makes it an agent rather than a pipeline.
From “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach” (Russell & Norvig, Ch. 2): An agent is anything that perceives its environment through sensors and acts upon it through actuators. In our research agent:
- Sensors: The tools that gather information (webSearch, readPage)
- Actuators: The tools that modify state or produce output (addToGraph, synthesizeReport)
- Agent Function: The LLM that maps percept sequences to actions
2.2 Agent State Management Patterns
State management is what separates a simple chatbot from an autonomous agent. Your agent must “remember” what it has learned across many iterations.
STATE MANAGEMENT ARCHITECTURE
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ EXTERNAL STATE │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Knowledge Graph │ │
│ │ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Node 1 │───▶│ Node 2 │───▶│ Node 3 │ │ │
│ │ │ IBM │ │ Quantum │ │ 1000 │ │ │
│ │ │ Quantum │ │ Error │ │ qubits │ │ │
│ │ └─────────┘ │Correction│ └─────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ └─────────┘ ▲ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ └──────────────┴──────────────┘ │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ▲ │
│ │ Tool calls update state │
│ │ │
│ ┌────────────────────────┴───────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ STATE SERIALIZER │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ Converts graph to text for LLM consumption: │ │
│ │ "Known facts: │ │
│ │ - IBM Quantum achieved 1000+ qubit processor │ │
│ │ - Quantum error correction was demonstrated │ │
│ │ Sources: [1] nature.com, [2] arxiv.org" │ │
│ └─────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ │ prepareStep injects │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ AGENT LOOP │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ User Query + Injected State ──▶ LLM ──▶ Tool Call │ │
│ │ │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
The State Lifecycle:
- Initialize: Start with empty knowledge graph
- Inject: Before each LLM call, serialize state into the prompt via
prepareStep - Update: After tool execution, update state with new information
- Persist: State lives outside the agent loop, surviving across iterations
// Conceptual state management pattern
interface AgentState {
knowledgeGraph: KnowledgeGraph;
sources: Source[];
confidenceScores: Map<string, number>;
iterationCount: number;
}
// The state is passed to prepareStep, which injects it into the prompt
const prepareStep = ({ state }: { state: AgentState }) => {
return {
messages: [
{
role: 'system',
content: `You have gathered the following information:
${serializeGraph(state.knowledgeGraph)}
Sources consulted: ${state.sources.length}
Current confidence: ${calculateOverallConfidence(state)}
Decide: Do you need more information, or is it time to synthesize?`
}
]
};
};
2.3 The prepareStep Callback and Context Injection
prepareStep is the AI SDK’s mechanism for dynamic context injection. It runs before each agent iteration, allowing you to inject accumulated knowledge into the prompt.
prepareStep EXECUTION FLOW
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ITERATION N │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ 1. BEFORE LLM CALL: prepareStep() executes │ │
│ │ - Reads current state (knowledge graph, sources) │ │
│ │ - Serializes state to text │ │
│ │ - Returns additional messages to inject │ │
│ └────────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ 2. LLM RECEIVES │ │
│ │ - Original user query │ │
│ │ - System prompt with tool descriptions │ │
│ │ - INJECTED: Current knowledge state ◀─── from prepareStep│ │
│ │ - Previous conversation history │ │
│ └────────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ 3. LLM DECIDES │ │
│ │ "Based on what I know, I should call webSearch() │ │
│ │ to learn about quantum error correction" │ │
│ └────────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ 4. TOOL EXECUTES │ │
│ │ - webSearch() returns results │ │
│ │ - Results added to state │ │
│ │ - STATE UPDATED ──▶ Will be visible in next prepareStep │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
ITERATION N+1
(prepareStep now sees updated state)
Why prepareStep Matters:
Without prepareStep, the LLM would have no memory of what it learned in previous iterations. Each tool call would be independent, with no accumulated context. This is the difference between:
- Stateless: “Search for quantum computing” -> results -> END
- Stateful: “Search for quantum computing” -> results -> “I found X, now let me search for related topic Y” -> results -> “I now know enough to synthesize” -> report
From “JavaScript: The Definitive Guide” (Flanagan, Ch. 13), this pattern mirrors async iterators where each iteration can depend on the results of previous iterations:
// The agent loop is conceptually an async iterator
async function* researchIterator(query: string) {
const state = initializeState();
while (!shouldStop(state)) {
// prepareStep equivalent: inject state
const context = serializeState(state);
// LLM decision
const action = await llmDecide(query, context);
// Execute and update state
const result = await executeAction(action);
updateState(state, result);
yield { action, result, state };
}
}
2.4 stopWhen for Intelligent Termination
How does an agent know when to stop researching and start writing? This is the “exploration vs. exploitation” tradeoff in AI. The stopWhen callback provides a mechanism for intelligent termination.
TERMINATION DECISION TREE
┌─────────────────┐
│ Agent State │
└────────┬────────┘
│
▼
┌────────────────────────────────┐
│ Enough information gathered? │
└────────────────┬───────────────┘
│
┌──────────────────┼──────────────────┐
│ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ Source Coverage │ │ Topic Coverage │ │ Confidence │
│ │ │ │ │ Threshold │
│ >= 3 credible │ │ All key aspects │ │ Overall >= 0.75 │
│ sources? │ │ addressed? │ │ │
└────────┬────────┘ └────────┬────────┘ └────────┬────────┘
│ │ │
└───────────────────┼───────────────────┘
│
▼
┌────────────────────────┐
│ ALL CONDITIONS MET? │
└────────────┬───────────┘
│
┌────────────┴────────────┐
│ │
▼ ▼
┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ YES: STOP │ │ NO: CONTINUE│
│ │ │ │
│ Call │ │ Search for │
│ synthesize │ │ more info │
│ Report() │ │ │
└──────────────┘ └──────────────┘
Implementation Approaches:
- LLM-Based Termination: Let the LLM decide by including a “done” tool
- Rule-Based Termination: Check explicit conditions (source count, confidence threshold)
- Hybrid: Combine both approaches
// stopWhen implementation
const stopWhen = ({ state, lastToolCall }: StopWhenArgs) => {
// Rule-based checks
if (state.sources.length < 3) return false;
if (state.overallConfidence < 0.75) return false;
// LLM-based check: Did the agent call synthesizeReport?
if (lastToolCall?.name === 'synthesizeReport') return true;
// Safety limit
if (state.iterationCount > 20) return true;
return false;
};
2.5 Knowledge Graphs: Nodes, Edges, and Queries
A knowledge graph represents information as entities (nodes) connected by relationships (edges). This structure enables the agent to understand how facts relate, not just what facts exist.
KNOWLEDGE GRAPH STRUCTURE
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
│ ┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ │
│ │ IBM Quantum │ │ Google Quantum│ │
│ │ [COMPANY] │ │ [COMPANY] │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ conf: 0.95 │ │ conf: 0.92 │ │
│ └───────┬───────┘ └───────┬───────┘ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ achieved │ demonstrated │
│ │ (2025-01) │ (2025-03) │
│ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌───────────────┐ enables ┌───────────────┐ │
│ │ 1000+ Qubit │◀────────────────▶ │ Error │ │
│ │ Processor │ │ Correction │ │
│ │ [MILESTONE] │ │ [TECHNIQUE] │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ conf: 0.88 │ │ conf: 0.91 │ │
│ └───────┬───────┘ └───────┬───────┘ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ impacts │ required_for │
│ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ │
│ │ Commercial │ │ Fault-Tolerant│ │
│ │ Quantum │◀─────────────────│ Computing │ │
│ │ [APPLICATION] │ enables │ [CONCEPT] │ │
│ │ conf: 0.72 │ │ conf: 0.85 │ │
│ └───────────────┘ └───────────────┘ │
│ │
│ Legend: ───▶ directed relationship │
│ ◀──▶ bidirectional relationship │
│ conf: confidence score (0-1) │
│ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
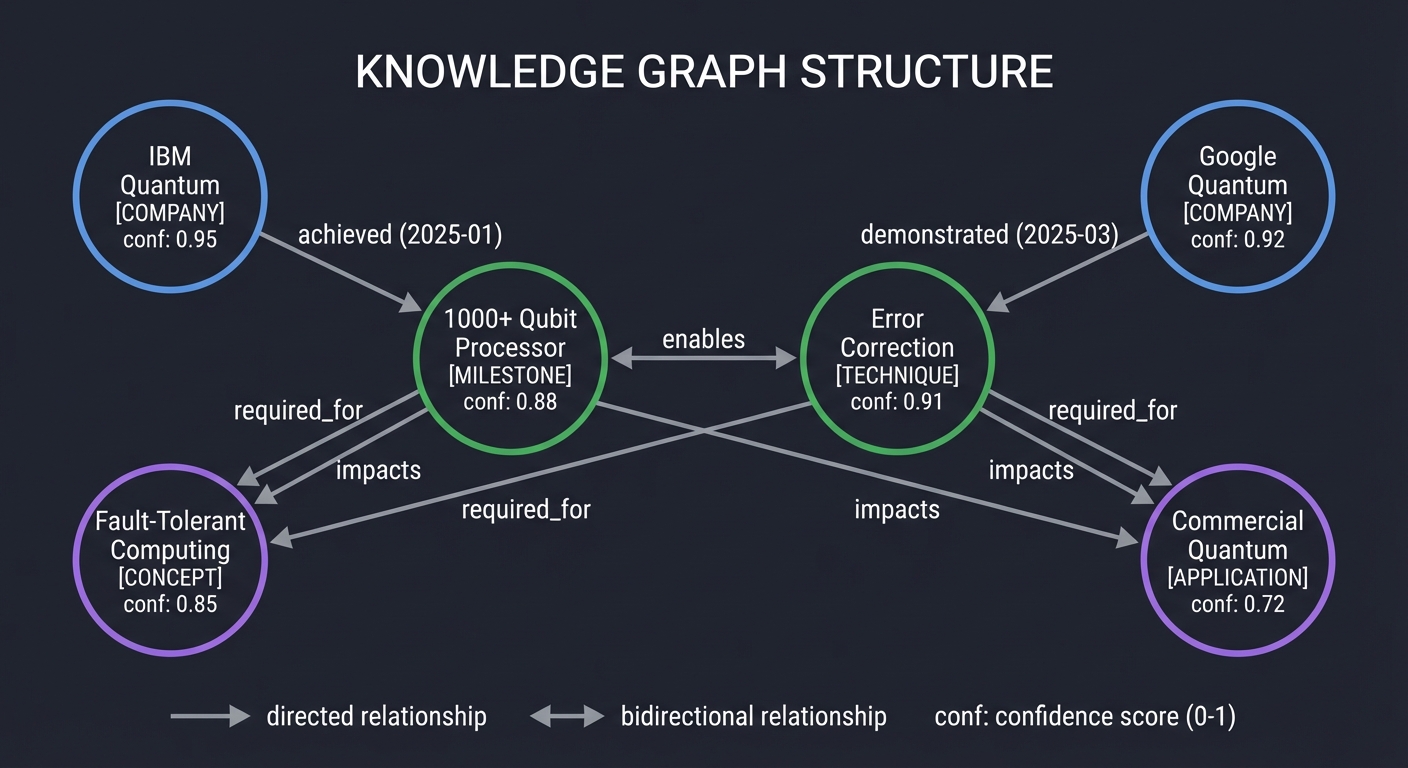
From “Graph Algorithms the Fun Way” (Kubica, Ch. 2-3):
Nodes (Vertices): Represent entities with properties
- Unique identifier
- Type (person, company, concept, event, technology)
- Name and description
- Confidence score
- Source URLs
Edges: Represent relationships
- Source and target node IDs
- Relationship type (achieved, enables, competes_with, published)
- Confidence score
- Source URL and timestamp
Graph Queries enable the agent to search its own memory:
- “What do I know about IBM?”
- “What technologies enable fault-tolerant computing?”
- “What sources mention error correction?”
// Knowledge graph data structures
interface KnowledgeNode {
id: string; // Unique identifier
type: 'entity' | 'concept' | 'event' | 'technology' | 'person' | 'company';
name: string; // Human-readable name
description: string; // Brief description
sourceUrls: string[]; // Where we learned this
confidence: number; // 0.0 to 1.0
metadata: Record<string, unknown>;
}
interface KnowledgeEdge {
id: string;
from: string; // Source node ID
to: string; // Target node ID
relation: string; // Relationship type
confidence: number;
sourceUrl: string;
timestamp: Date;
}
interface KnowledgeGraph {
nodes: Map<string, KnowledgeNode>;
edges: KnowledgeEdge[];
// Query methods
findNodesByType(type: string): KnowledgeNode[];
findRelatedNodes(nodeId: string): KnowledgeNode[];
getEdgesBetween(nodeId1: string, nodeId2: string): KnowledgeEdge[];
searchByName(query: string): KnowledgeNode[];
getNodesBySource(url: string): KnowledgeNode[];
}
2.6 Confidence Scoring and Source Evaluation
Not all information is equally reliable. Your agent must assess the credibility of sources and assign confidence scores to facts.
CONFIDENCE SCORING MODEL
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ SOURCE CREDIBILITY │
│ │
│ Domain Type Base Score Examples │
│ ───────────────── ────────── ───────────────────── │
│ Academic (.edu) 0.90 mit.edu, stanford.edu │
│ Government (.gov) 0.88 nasa.gov, nih.gov │
│ Scientific journals 0.95 nature.com, science.org │
│ Major news outlets 0.75 nytimes.com, bbc.com │
│ Tech companies 0.70 google.ai, microsoft.com │
│ Wikipedia 0.65 wikipedia.org │
│ Blogs/personal 0.40 medium.com, substack.com │
│ Unknown 0.30 anything else │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ CONFIDENCE MODIFIERS │
│ │
│ Factor Modifier Application │
│ ───────────────── ───────── ───────────────────── │
│ Corroboration +0.10 Per additional source │
│ Recency (< 3 months) +0.05 For time-sensitive topics │
│ Recency (> 1 year) -0.10 For time-sensitive topics │
│ Specificity +0.05 Includes data/citations │
│ Contradiction -0.15 Conflicting sources │
│ Author expertise +0.10 Known expert in field │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
FINAL CONFIDENCE CALCULATION
confidence = base_score
+ (corroboration_count * 0.10)
+ recency_modifier
+ specificity_bonus
- contradiction_penalty
confidence = clamp(confidence, 0.0, 1.0)
2.7 The ReAct Pattern Applied to Research
ReAct (Reasoning and Acting) is the academic foundation for tool-using agents. It alternates between reasoning (thinking about what to do) and acting (executing tools).
ReAct PATTERN IN RESEARCH AGENT
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ITERATION 1 │
│ │
│ THOUGHT: "I need to find recent articles about quantum │
│ computing breakthroughs to answer the user's │
│ question." │
│ │
│ ACTION: webSearch("quantum computing breakthroughs 2025") │
│ │
│ OBSERVATION: Found 15 results including nature.com, │
│ arxiv.org, ibm.com articles │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ITERATION 2 │
│ │
│ THOUGHT: "The Nature article looks most credible. │
│ I should read it to extract key facts." │
│ │
│ ACTION: readPage("https://nature.com/quantum-2025") │
│ │
│ OBSERVATION: Article discusses IBM achieving 1000 qubits, │
│ Google demonstrating error correction │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ITERATION 3 │
│ │
│ THOUGHT: "I should extract structured facts from this │
│ article and add them to my knowledge graph." │
│ │
│ ACTION: extractFacts(article_content) │
│ addToGraph(extracted_facts) │
│ │
│ OBSERVATION: Added 5 nodes and 7 edges to knowledge graph │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ITERATION N │
│ │
│ THOUGHT: "I have gathered information from 5 credible │
│ sources, covering error correction, qubit scaling, │
│ and commercial applications. My overall confidence │
│ is 0.82. It's time to synthesize the report." │
│ │
│ ACTION: synthesizeReport() │
│ │
│ OBSERVATION: Generated 2-page report with 12 citations │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
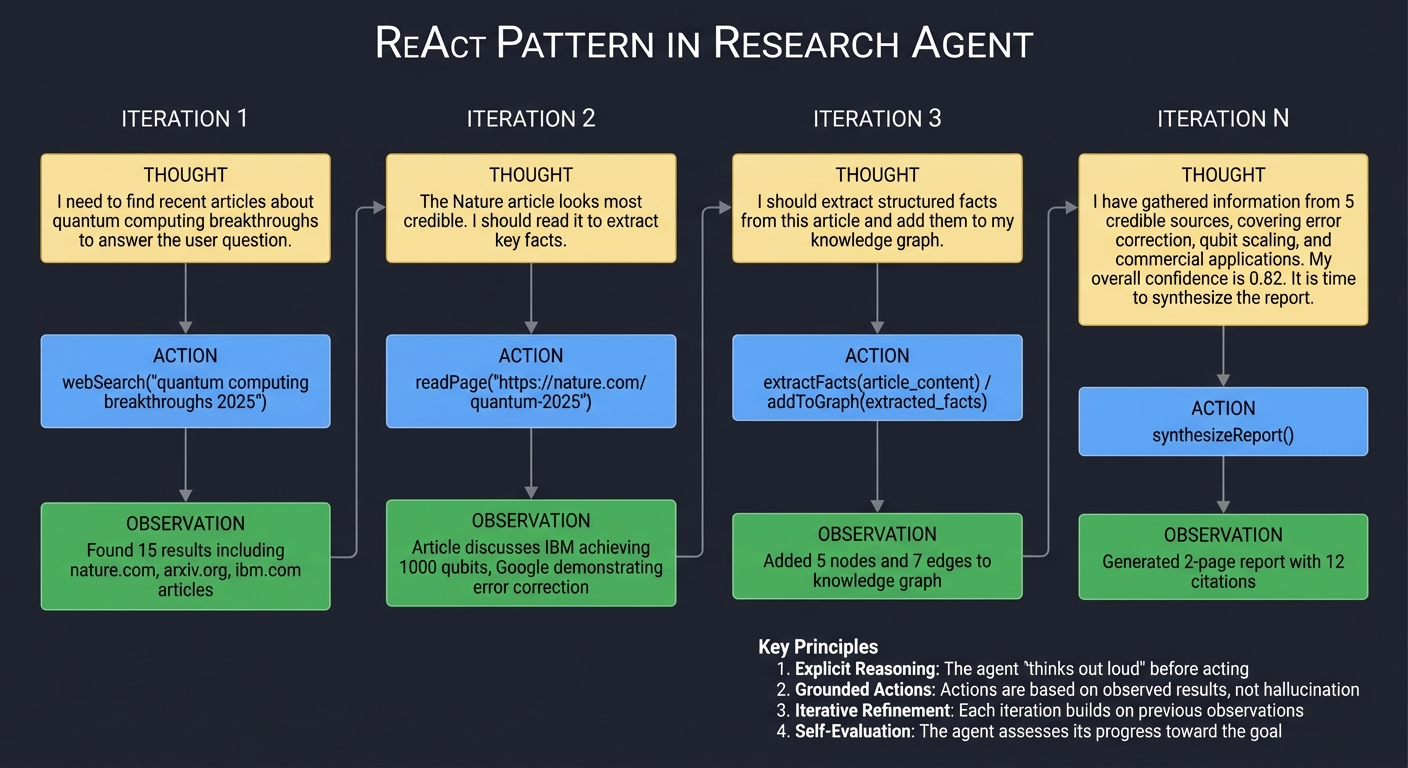
Key ReAct Principles:
- Explicit Reasoning: The agent “thinks out loud” before acting
- Grounded Actions: Actions are based on observed results, not hallucination
- Iterative Refinement: Each iteration builds on previous observations
- Self-Evaluation: The agent assesses its progress toward the goal
3. Complete Project Specification
3.1 What You Will Build
A command-line research agent that:
- Takes a research question as input
- Autonomously searches the web for relevant information
- Reads and extracts facts from web pages
- Builds a knowledge graph of discovered information
- Decides when enough research has been gathered
- Synthesizes a comprehensive report with citations and confidence scores
3.2 Functional Requirements
- Research Initialization
- Accept a research question via CLI
- Initialize empty knowledge graph
- Set confidence thresholds and iteration limits
- Web Search Integration
- Search the web for relevant pages
- Filter results by credibility
- Track which URLs have been visited
- Content Extraction
- Fetch and parse web pages
- Extract key facts using
generateObject - Assign confidence scores based on source credibility
- Knowledge Graph Management
- Add nodes (entities, concepts, events)
- Add edges (relationships between nodes)
- Query the graph for related information
- Detect and flag contradictions
- Autonomous Decision Making
- Decide which search queries to execute
- Choose which pages to read in depth
- Determine when enough information is gathered
- Balance exploration vs. synthesis
- Report Generation
- Synthesize findings into structured report
- Include inline citations
- Show confidence scores for claims
- Visualize knowledge graph connections
3.3 Non-Functional Requirements
- Robustness: Handle API failures, rate limits, and malformed content gracefully
- Observability: Log each step with reasoning for debugging and learning
- Configurability: Allow customization of confidence thresholds, iteration limits, and search parameters
- Reproducibility: Given the same query, produce consistent (though not identical) results
3.4 Tool Specifications
| Tool | Purpose | Input Schema | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
webSearch |
Find relevant URLs | { query: string, limit?: number } |
Array of { url, title, snippet } |
readPage |
Extract page content | { url: string } |
{ content: string, metadata: {...} } |
extractFacts |
Parse content into facts | { content: string, sourceUrl: string } |
Array of structured facts |
addToGraph |
Store facts in graph | { nodes: [...], edges: [...] } |
Updated graph statistics |
queryGraph |
Search accumulated knowledge | { query: string } |
Related nodes and edges |
synthesizeReport |
Generate final output | { format?: string } |
Formatted research report |
4. Real World Outcome
4.1 Example CLI Session
$ research "What are the latest breakthroughs in quantum computing as of 2025?"
╔═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ RESEARCH AGENT INITIALIZED ║
╠═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╣
║ Query: What are the latest breakthroughs in quantum computing... ║
║ Knowledge graph: 0 nodes, 0 edges ║
║ Confidence threshold: 0.75 ║
║ Max iterations: 20 ║
╚═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝
[Step 1] REASONING
"I need to find recent articles about quantum computing
breakthroughs to answer the user's question."
[Step 1] ACTION: webSearch("quantum computing breakthroughs 2025")
Found 15 results
├── nature.com/quantum-error-correction-2025 (credibility: 0.95)
├── arxiv.org/abs/2501.12345 (credibility: 0.90)
├── ibm.com/quantum/announcements (credibility: 0.70)
└── ... 12 more results
[Step 2] REASONING
"The Nature article has the highest credibility score.
I should read it first to establish a foundation."
[Step 2] ACTION: readPage("https://nature.com/quantum-error-correction-2025")
Fetched 15,234 characters
Title: "Breakthrough in Quantum Error Correction Enables..."
[Step 3] ACTION: extractFacts(content)
Extracted 12 facts:
├── Entity: IBM Quantum (type: company)
├── Entity: Google Quantum AI (type: company)
├── Milestone: 1000+ qubit processor (achieved: 2025-01)
├── Technique: Surface code error correction (demonstrated: 2025-03)
└── ... 8 more facts
[Step 4] ACTION: addToGraph(facts)
Knowledge graph updated:
├── Nodes: 12 (was 0)
├── Edges: 8 (was 0)
└── Sources: 1
[Step 5] REASONING
"I have information about IBM and Google's achievements.
Let me search specifically for commercial applications
to get a more complete picture."
[Step 5] ACTION: webSearch("quantum computing commercial applications 2025")
Found 10 results
├── mckinsey.com/quantum-commercial-outlook (credibility: 0.72)
├── techcrunch.com/quantum-startups-2025 (credibility: 0.65)
└── ... 8 more results
[Step 6] ACTION: readPage("https://mckinsey.com/quantum-commercial-outlook")
Fetched 22,456 characters
[Step 7] ACTION: extractFacts(content)
Extracted 8 new facts, 2 corroborate existing knowledge:
├── UPDATE: "1000+ qubit processor" confidence: 0.88 -> 0.93 (+corroboration)
├── NEW: Commercial applications in drug discovery
└── ... 6 more facts
[Step 8] ACTION: addToGraph(facts)
Knowledge graph updated:
├── Nodes: 18 (was 12)
├── Edges: 15 (was 8)
└── Sources: 2
... [Steps 9-11 omitted for brevity] ...
[Step 12] REASONING
"I have gathered sufficient information from 5 credible sources.
My knowledge covers:
- Error correction advances (confidence: 0.92)
- Qubit scaling milestones (confidence: 0.88)
- Commercial applications (confidence: 0.78)
- Competition landscape (confidence: 0.85)
Overall confidence: 0.86 (exceeds threshold of 0.75)
Time to synthesize the research report."
[Step 13] ACTION: synthesizeReport()
╔═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ RESEARCH REPORT: QUANTUM COMPUTING 2025 ║
╠═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╣
## Executive Summary
Quantum computing achieved several major milestones in 2025, with
breakthroughs in error correction, qubit scaling, and the emergence
of first commercial applications. IBM and Google remain the leading
players, with both achieving significant advances in fault-tolerant
quantum computing. [1][2][3]
## Key Findings
### 1. Error Correction Breakthrough (High Confidence: 0.92)
Google Quantum AI demonstrated surface code error correction with
logical error rates below physical qubit error rates for the first
time, a critical milestone for fault-tolerant quantum computing. [1]
IBM independently verified similar results using their Heavy Hex
qubit topology. [2]
### 2. Qubit Scaling Milestone (High Confidence: 0.88)
IBM announced their Condor processor exceeding 1,000 qubits in
January 2025, making it the first quantum processor to break the
kilobit barrier. [2] However, experts note that qubit count alone
is not indicative of computational advantage. [3]
### 3. Commercial Applications Emerge (Medium Confidence: 0.78)
First production use cases appeared in:
- Drug discovery: Simulating molecular interactions [4]
- Financial modeling: Portfolio optimization [5]
- Materials science: Battery design [4]
These applications remain limited to problems where quantum computers
provide provable advantages over classical systems.
### 4. Competition Landscape (High Confidence: 0.85)
The quantum computing race intensified with:
- IBM and Google leading in superconducting qubits
- IonQ advancing trapped ion technology
- PsiQuantum pursuing photonic quantum computing
- Chinese institutions reporting competitive results [3][5]
## Knowledge Graph Visualization
┌─────────────────┐ achieved ┌──────────────────────┐
│ IBM Quantum │ ───────────────────▶│ 1000+ qubit proc. │
│ (company) │ │ (milestone) │
│ conf: 0.95 │ │ conf: 0.93 │
└────────┬────────┘ └──────────────────────┘
│ │
│ competes_with │ enables
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────┐ published ┌──────────────────────┐
│ Google Quantum │ ───────────────────▶│ Surface code error │
│ AI │ │ correction │
│ (company) │ │ (technique) │
│ conf: 0.92 │ │ conf: 0.91 │
└─────────────────┘ └──────────┬───────────┘
│
│ required_for
▼
┌──────────────────────┐
│ Fault-tolerant │
│ quantum computing │
│ (concept) │
│ conf: 0.85 │
└──────────────────────┘
## Confidence Assessment
| Topic | Confidence | Sources |
|------------------------|------------|---------|
| Error correction | 0.92 | 3 |
| Qubit scaling | 0.88 | 2 |
| Commercial applications| 0.78 | 2 |
| Competition landscape | 0.85 | 4 |
| **Overall** | **0.86** | **5** |
## Sources
[1] Nature: "Quantum Error Correction Advances" (2025-03-15)
Confidence: 0.95 | Type: Academic Journal
https://nature.com/quantum-error-correction-2025
[2] IBM Research: "Condor Quantum Processor Announcement" (2025-01-08)
Confidence: 0.88 | Type: Corporate/Research
https://research.ibm.com/quantum/condor
[3] ArXiv: "Comparative Analysis of Quantum Computing Platforms" (2025-02-22)
Confidence: 0.90 | Type: Preprint
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.12345
[4] McKinsey: "Quantum Computing Commercial Outlook 2025" (2025-04-10)
Confidence: 0.72 | Type: Industry Analysis
https://mckinsey.com/quantum-commercial-outlook
[5] MIT Technology Review: "The State of Quantum 2025" (2025-05-01)
Confidence: 0.78 | Type: Tech Journalism
https://technologyreview.com/quantum-state-2025
╚═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝
📊 Research Statistics
├── Total iterations: 13
├── Web searches: 4
├── Pages read: 5
├── Facts extracted: 42
├── Knowledge graph: 24 nodes, 31 edges
└── Time elapsed: 2m 34s
📁 Files saved:
├── research_quantum_2025-12-22.md (full report)
├── knowledge_graph.json (graph export)
└── research_log.json (detailed execution log)
5. Solution Architecture
5.1 High-Level Architecture
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ RESEARCH AGENT SYSTEM │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ USER INTERFACE │ │
│ │ CLI: research "query" │ │
│ │ Output: Progress updates, final report │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────┬────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ AGENT ORCHESTRATOR │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ prepareStep │───▶│ AI SDK │───▶│ Tool Executor │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ agent() │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ Injects │ │ │ │ Dispatches to │ │ │
│ │ │ state into │ │ Decides next │ │ appropriate │ │ │
│ │ │ context │ │ action │ │ tool │ │ │
│ │ └─────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └────────┬────────┘ │ │
│ │ ▲ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ ┌──────┴───┴───────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ STATE MANAGER │ │ │
│ │ │ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ Knowledge Graph │ │ Source Registry │ │ Confidence │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ Calculator │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ Nodes + Edges │ │ URL -> metadata │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────┘ │ │ │
│ │ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ TOOL REGISTRY │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ │ │
│ │ │webSearch │ │readPage │ │extract │ │addTo │ │synthesize│ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │Facts │ │Graph │ │Report │ │ │
│ │ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ ▼ ▼ ▼ ▼ ▼ │ │
│ │ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ │ │
│ │ │Search API│ │Fetch API │ │generateO │ │Graph DB │ │generateO │ │ │
│ │ │(external)│ │(external)│ │bject() │ │(in-mem) │ │bject() │ │ │
│ │ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
5.2 Knowledge Graph Data Structures
// Core types for the knowledge graph
// Node types
type NodeType =
| 'entity' // General entity (person, place, thing)
| 'company' // Organization
| 'person' // Individual
| 'concept' // Abstract idea
| 'technology' // Technical capability
| 'event' // Something that happened
| 'milestone' // Achievement or target
| 'technique'; // Method or approach
// Relationship types
type RelationType =
| 'achieved' // Entity achieved milestone
| 'published' // Entity published research
| 'enables' // X enables Y
| 'required_for' // X is required for Y
| 'competes_with' // X competes with Y
| 'part_of' // X is part of Y
| 'uses' // X uses Y
| 'contradicts' // X contradicts Y
| 'corroborates'; // X supports Y
interface KnowledgeNode {
id: string;
type: NodeType;
name: string;
description: string;
sourceUrls: string[];
confidence: number;
createdAt: Date;
updatedAt: Date;
metadata: {
aliases?: string[]; // Alternative names
dates?: string[]; // Relevant dates
quantities?: number[]; // Relevant numbers
tags?: string[]; // Classification tags
};
}
interface KnowledgeEdge {
id: string;
from: string; // Source node ID
to: string; // Target node ID
relation: RelationType;
confidence: number;
sourceUrl: string;
createdAt: Date;
metadata: {
evidence?: string; // Supporting text
temporal?: {
startDate?: Date;
endDate?: Date;
};
};
}
interface Source {
url: string;
title: string;
credibility: number;
domain: string;
fetchedAt: Date;
contentLength: number;
factsExtracted: number;
}
interface AgentState {
knowledgeGraph: {
nodes: Map<string, KnowledgeNode>;
edges: KnowledgeEdge[];
};
sources: Map<string, Source>;
visitedUrls: Set<string>;
searchQueries: string[];
iterationCount: number;
startedAt: Date;
}
5.3 Tool Registry Design
import { z } from 'zod';
import { tool } from 'ai';
// Tool definitions with Zod schemas
const webSearchTool = tool({
description: 'Search the web for information on a topic. Returns a list of relevant URLs with titles and snippets.',
parameters: z.object({
query: z.string().describe('The search query'),
limit: z.number().optional().default(10).describe('Maximum results to return')
}),
execute: async ({ query, limit }) => {
// Implementation calls search API
return searchResults;
}
});
const readPageTool = tool({
description: 'Fetch and extract text content from a web page URL.',
parameters: z.object({
url: z.string().url().describe('The URL to fetch')
}),
execute: async ({ url }) => {
// Implementation fetches and parses page
return { content, metadata };
}
});
const extractFactsTool = tool({
description: 'Extract structured facts from text content using AI. Returns entities, relationships, and claims.',
parameters: z.object({
content: z.string().describe('The text content to analyze'),
sourceUrl: z.string().url().describe('The source URL for attribution')
}),
execute: async ({ content, sourceUrl }) => {
// Uses generateObject to extract structured facts
return { nodes, edges };
}
});
const addToGraphTool = tool({
description: 'Add extracted facts to the knowledge graph. Merges with existing nodes and updates confidence scores.',
parameters: z.object({
nodes: z.array(z.object({
name: z.string(),
type: z.string(),
description: z.string()
})),
edges: z.array(z.object({
from: z.string(),
to: z.string(),
relation: z.string()
}))
}),
execute: async ({ nodes, edges }) => {
// Updates agent state with new facts
return { nodesAdded, edgesAdded, nodesUpdated };
}
});
const queryGraphTool = tool({
description: 'Search the accumulated knowledge graph for information. Use this to check what you already know before searching the web.',
parameters: z.object({
query: z.string().describe('What to search for in the knowledge graph')
}),
execute: async ({ query }) => {
// Searches nodes and edges by name/description
return { matchingNodes, relatedEdges };
}
});
const synthesizeReportTool = tool({
description: 'Generate the final research report from accumulated knowledge. Call this when you have gathered sufficient information.',
parameters: z.object({
format: z.enum(['markdown', 'json', 'text']).optional().default('markdown'),
includeGraph: z.boolean().optional().default(true)
}),
execute: async ({ format, includeGraph }) => {
// Generates structured report with citations
return { report, citations, graphVisualization };
}
});
5.4 File Structure Recommendation
research-agent/
├── src/
│ ├── index.ts # CLI entry point
│ ├── agent/
│ │ ├── orchestrator.ts # Main agent loop using AI SDK
│ │ ├── prepareStep.ts # Context injection logic
│ │ ├── stopWhen.ts # Termination conditions
│ │ └── state.ts # State management
│ ├── tools/
│ │ ├── index.ts # Tool registry
│ │ ├── webSearch.ts # Search implementation
│ │ ├── readPage.ts # Page fetching
│ │ ├── extractFacts.ts # Fact extraction with generateObject
│ │ ├── addToGraph.ts # Graph updates
│ │ ├── queryGraph.ts # Graph queries
│ │ └── synthesizeReport.ts # Report generation
│ ├── graph/
│ │ ├── types.ts # Node, Edge, Graph types
│ │ ├── KnowledgeGraph.ts # Graph implementation
│ │ ├── confidence.ts # Confidence calculations
│ │ └── serializer.ts # Graph <-> text conversion
│ ├── schemas/
│ │ ├── fact.ts # Zod schema for facts
│ │ ├── report.ts # Zod schema for reports
│ │ └── citation.ts # Zod schema for citations
│ └── utils/
│ ├── credibility.ts # Source credibility scoring
│ ├── logger.ts # Step-by-step logging
│ └── formatting.ts # Output formatting
├── tests/
│ ├── unit/
│ │ ├── graph.test.ts
│ │ ├── confidence.test.ts
│ │ └── credibility.test.ts
│ ├── integration/
│ │ ├── agent.test.ts
│ │ └── tools.test.ts
│ └── mocks/
│ ├── searchApi.ts
│ └── fetchApi.ts
├── package.json
├── tsconfig.json
└── README.md
6. Phased Implementation Guide
Phase 1: Foundation (Days 1-4)
Goals:
- Set up project structure and dependencies
- Implement basic agent loop with AI SDK
- Create simple webSearch and readPage tools
Tasks:
- Initialize TypeScript project with AI SDK
- Create basic CLI that accepts a query
- Implement webSearch tool (can use mock data initially)
- Implement readPage tool (can use mock data initially)
- Create minimal agent loop that searches and reads one page
Milestone Checkpoint:
$ npm run dev "quantum computing"
# Agent searches, reads one page, outputs raw content
Phase 2: State Management (Days 5-8)
Goals:
- Implement knowledge graph data structure
- Add
prepareStepfor context injection - Create fact extraction with
generateObject
Tasks:
- Define TypeScript types for nodes and edges
- Implement KnowledgeGraph class with CRUD operations
- Create extractFacts tool using
generateObject - Implement prepareStep that serializes graph to text
- Update agent loop to use prepareStep
Milestone Checkpoint:
$ npm run dev "quantum computing"
# Agent now "remembers" facts across iterations
# prepareStep injects: "You have learned: [facts]"
Phase 3: Intelligent Termination (Days 9-12)
Goals:
- Implement confidence scoring
- Add
stopWhenfor autonomous termination - Create synthesizeReport tool
Tasks:
- Implement source credibility scoring
- Add confidence calculation for facts
- Implement stopWhen with multiple conditions
- Create synthesizeReport tool with citations
- Add graph visualization to report
Milestone Checkpoint:
$ npm run dev "quantum computing"
# Agent autonomously decides when to stop
# Produces formatted report with citations
Phase 4: Production Quality (Days 13-18)
Goals:
- Real API integrations
- Robust error handling
- Testing and polish
Tasks:
- Integrate real search API (e.g., Tavily, Serper)
- Implement proper page fetching with error handling
- Add rate limiting and retry logic
- Write comprehensive tests
- Add detailed logging and progress output
- Create export formats (markdown, JSON)
Milestone Checkpoint:
$ npm run dev "What are the latest AI breakthroughs?"
# Full working system with real web search
# Produces professional research report
Phase 5: Extensions (Days 19-21)
Goals:
- Add queryGraph tool for self-reflection
- Implement contradiction detection
- Add graph export and visualization
Tasks:
- Implement queryGraph tool
- Add contradiction detection to addToGraph
- Create JSON export for external visualization
- Add ASCII graph visualization
- Write documentation
7. Testing Strategy
7.1 Unit Tests
// tests/unit/graph.test.ts
describe('KnowledgeGraph', () => {
it('should add nodes and update confidence on duplicate', () => {
const graph = new KnowledgeGraph();
graph.addNode({
name: 'IBM Quantum',
type: 'company',
confidence: 0.8,
sourceUrls: ['https://nature.com/article1']
});
// Add same node from different source
graph.addNode({
name: 'IBM Quantum',
type: 'company',
confidence: 0.7,
sourceUrls: ['https://arxiv.org/paper1']
});
const node = graph.findByName('IBM Quantum');
expect(node.confidence).toBeGreaterThan(0.8); // Corroboration boost
expect(node.sourceUrls).toHaveLength(2);
});
it('should detect contradictions', () => {
const graph = new KnowledgeGraph();
graph.addEdge({
from: 'IBM',
to: 'Condor',
relation: 'achieved',
metadata: { evidence: '1000 qubits in 2025' }
});
// Contradicting information
graph.addEdge({
from: 'IBM',
to: 'Condor',
relation: 'achieved',
metadata: { evidence: '500 qubits in 2025' }
});
expect(graph.getContradictions()).toHaveLength(1);
});
});
7.2 Mocking Web Search and Fetch
// tests/mocks/searchApi.ts
export const mockSearchResults = {
'quantum computing': [
{
url: 'https://nature.com/quantum-2025',
title: 'Quantum Error Correction Advances',
snippet: 'Major breakthrough in surface codes...'
},
{
url: 'https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.12345',
title: 'Scaling Quantum Processors',
snippet: 'IBM announces 1000+ qubit processor...'
}
]
};
export const mockPageContent = {
'https://nature.com/quantum-2025': {
content: `Google Quantum AI demonstrated surface code error correction
with logical error rates below physical qubit error rates.
IBM independently verified similar results using Heavy Hex.`,
metadata: { title: 'Quantum Error Correction', publishDate: '2025-03-15' }
}
};
// Use in tests
jest.mock('../src/api/search', () => ({
searchWeb: jest.fn((query) => mockSearchResults[query] || [])
}));
7.3 Integration Testing
// tests/integration/agent.test.ts
describe('Research Agent Integration', () => {
it('should complete research loop and produce report', async () => {
const agent = createResearchAgent({
maxIterations: 10,
confidenceThreshold: 0.6,
useMocks: true
});
const result = await agent.research('quantum computing breakthroughs');
expect(result.report).toBeDefined();
expect(result.citations.length).toBeGreaterThan(0);
expect(result.graph.nodes.size).toBeGreaterThan(0);
expect(result.iterationCount).toBeLessThanOrEqual(10);
});
it('should stop when confidence threshold is reached', async () => {
const agent = createResearchAgent({
maxIterations: 20,
confidenceThreshold: 0.8,
useMocks: true
});
const result = await agent.research('quantum computing');
expect(result.overallConfidence).toBeGreaterThanOrEqual(0.8);
});
});
7.4 Knowledge Graph Operations Testing
// tests/unit/graphOperations.test.ts
describe('Graph Queries', () => {
let graph: KnowledgeGraph;
beforeEach(() => {
graph = new KnowledgeGraph();
// Set up test data
graph.addNode({ id: 'ibm', name: 'IBM Quantum', type: 'company' });
graph.addNode({ id: 'google', name: 'Google Quantum', type: 'company' });
graph.addNode({ id: 'error-correction', name: 'Error Correction', type: 'technique' });
graph.addEdge({ from: 'ibm', to: 'error-correction', relation: 'uses' });
graph.addEdge({ from: 'google', to: 'error-correction', relation: 'demonstrated' });
});
it('should find nodes by type', () => {
const companies = graph.findNodesByType('company');
expect(companies).toHaveLength(2);
});
it('should find related nodes', () => {
const related = graph.findRelatedNodes('error-correction');
expect(related.map(n => n.name)).toContain('IBM Quantum');
expect(related.map(n => n.name)).toContain('Google Quantum');
});
it('should search by name fragment', () => {
const results = graph.searchByName('quantum');
expect(results).toHaveLength(2);
});
});
8. Common Pitfalls and Debugging
8.1 Frequent Mistakes with Complex Agents
| Pitfall | Symptom | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| State not persisting | Agent forgets previous findings | Ensure state is passed correctly to prepareStep and updated after tool calls |
| Infinite loops | Agent never stops researching | Implement robust stopWhen with maxSteps fallback |
| Context overflow | LLM errors or truncation | Summarize knowledge graph instead of including all details |
| Tool call failures | Agent crashes on API errors | Wrap all tool executions in try-catch, return error messages to LLM |
| Duplicate facts | Same information stored multiple times | Implement deduplication in addToGraph based on semantic similarity |
| Poor source credibility | Low-quality citations in report | Filter sources by credibility score before reading |
| Slow execution | Research takes too long | Parallelize search queries, cache page content |
8.2 Debugging Strategies
1. Enable verbose logging:
const agent = createAgent({
onStepStart: (step) => console.log(`[Step ${step.index}] Starting...`),
onToolCall: (tool, args) => console.log(` Tool: ${tool}(${JSON.stringify(args)})`),
onToolResult: (result) => console.log(` Result: ${JSON.stringify(result).slice(0, 200)}...`),
onStepEnd: (step, state) => console.log(` State: ${state.knowledgeGraph.nodes.size} nodes`)
});
2. Inspect prepareStep output:
const prepareStep = ({ state }) => {
const injectedContext = serializeGraph(state.knowledgeGraph);
console.log('=== INJECTED CONTEXT ===');
console.log(injectedContext);
console.log('========================');
return { messages: [{ role: 'system', content: injectedContext }] };
};
3. Validate tool schemas:
// Ensure Zod schemas match expected tool behavior
const testFactExtraction = async () => {
const result = await extractFactsTool.execute({
content: 'IBM achieved 1000 qubits.',
sourceUrl: 'https://example.com'
});
console.log('Extracted facts:', JSON.stringify(result, null, 2));
// Verify shape matches expectations
};
4. Test termination conditions in isolation:
describe('stopWhen', () => {
it('should continue when confidence is low', () => {
const state = createMockState({ confidence: 0.5 });
expect(stopWhen({ state })).toBe(false);
});
it('should stop when confidence threshold reached', () => {
const state = createMockState({ confidence: 0.85 });
expect(stopWhen({ state })).toBe(true);
});
});
8.3 Common Agent Behavior Issues
Issue: Agent keeps searching instead of reading pages
Diagnosis: The LLM prefers searching because it sees immediate results.
Solution: Modify system prompt to emphasize depth over breadth:
const systemPrompt = `
You are a thorough research agent. Before searching for new information,
you should FIRST read pages you have already discovered. Only search
for new topics when you have read at least 2-3 pages on the current topic.
`;
Issue: Agent synthesizes too early
Diagnosis: The stopWhen threshold is too permissive.
Solution: Require minimum source diversity:
const stopWhen = ({ state }) => {
if (state.sources.size < 3) return false; // Minimum 3 unique sources
if (state.knowledgeGraph.nodes.size < 10) return false; // Minimum 10 facts
return state.overallConfidence >= 0.75;
};
Issue: Knowledge graph has disconnected nodes
Diagnosis: extractFacts is not creating edges between entities.
Solution: Improve the fact extraction schema:
const factSchema = z.object({
entities: z.array(z.object({
name: z.string(),
type: z.string(),
description: z.string()
})),
relationships: z.array(z.object({
subject: z.string().describe('Must match an entity name'),
predicate: z.string(),
object: z.string().describe('Must match an entity name')
})).describe('Extract ALL relationships between entities mentioned in the text')
});
9. Extensions and Challenges
9.1 Beginner Extensions
- Add a
queryGraphtool: Let the agent search its own memory before searching the web - Implement source deduplication: Avoid reading the same content from different URLs
- Add export formats: Generate JSON, HTML, or PDF versions of the report
9.2 Intermediate Extensions
- Contradiction detection and resolution: Flag when sources disagree and present both views
- Multi-query research: Accept multiple related queries and cross-reference findings
- Incremental research: Resume research from a saved state
- Graph visualization: Export to Graphviz DOT format or use D3.js for interactive visualization
9.3 Advanced Extensions
- Persistent knowledge base: Use SQLite or Neo4j to store knowledge across sessions
- Multi-agent research: Spawn sub-agents for parallel topic exploration
- Fact verification pipeline: Cross-check claims against authoritative sources
- Research planning: Generate and follow a research outline before diving into details
9.4 Challenge Problems
-
The Wikipedia Challenge: Given a topic, build a knowledge graph that matches Wikipedia’s article structure for that topic.
-
The Debate Challenge: Research both sides of a controversial topic and present balanced arguments with evidence.
-
The Update Challenge: Given an existing research report, find new developments and update the report incrementally.
10. Resources
10.1 Essential Reading
| Topic | Resource | Specific Sections |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Graphs | “Graph Algorithms the Fun Way” by Jeremy Kubica | Ch. 2-3: Graph representation, traversal |
| Agent Architecture | “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach” by Russell & Norvig | Ch. 2: Intelligent Agents |
| Async Iteration | “JavaScript: The Definitive Guide” by David Flanagan | Ch. 13: Async Iteration and Generators |
| ReAct Pattern | “ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting” (Yao et al., 2022) | Full paper |
| AI SDK | AI SDK Documentation | Agents section |
| State Patterns | “Fluent Python, 2nd Edition” by Luciano Ramalho | Ch. 22: State patterns (concepts apply to TS) |
10.2 Academic Papers
- ReAct: Yao, S., et al. (2022). “ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models”
- Toolformer: Schick, T., et al. (2023). “Toolformer: Language Models Can Teach Themselves to Use Tools”
- Chain-of-Thought: Wei, J., et al. (2022). “Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models”
10.3 Tools and Libraries
- AI SDK: https://sdk.vercel.ai/ - The core framework
- Zod: https://zod.dev/ - Runtime type validation
- Tavily API: https://tavily.com/ - AI-optimized search API
- Cheerio: https://cheerio.js.org/ - HTML parsing for readPage
- Vis.js: https://visjs.org/ - Graph visualization
10.4 Related Projects in This Series
- Previous: Project 4 (Agentic Tool Selection) - Foundation for multi-tool agents
- Next: Project 6 (Multi-Modal Pipeline) - Extends to images and audio
- Related: Project 8 (Prompt Optimization) - Improve agent reasoning quality
11. Self-Assessment Checklist
Understanding Verification
- I can explain the difference between a simple LLM call and an autonomous agent
- I can describe what
prepareStepdoes and why it is necessary for stateful agents - I can explain how
stopWhendetermines when the agent should terminate - I can describe the structure of a knowledge graph (nodes, edges, properties)
- I can explain the ReAct pattern and identify the Thought/Action/Observation cycle in my implementation
- I can describe at least 3 factors that affect source credibility scoring
- I can explain how confidence scores are calculated and updated
Implementation Verification
- My agent correctly chains multiple tool calls to gather information
prepareStepsuccessfully injects accumulated knowledge before each LLM call- The agent terminates appropriately when conditions are met (not too early, not infinite)
- Facts are correctly extracted and stored in the knowledge graph
- The final report includes inline citations linked to sources
- Confidence scores are visible in the output
- Error handling prevents crashes on API failures
Integration Verification
- I can run the agent with a real search API (not just mocks)
- The agent produces useful research on topics I did not test during development
- Logs clearly show the agent’s reasoning at each step
- I can export the knowledge graph to JSON for external use
Growth Verification
- I debugged at least one issue by inspecting
prepareStepoutput - I adjusted
stopWhenconditions based on observed agent behavior - I improved fact extraction by modifying the Zod schema
- I can now design multi-tool agents for other domains
12. Completion Criteria
Minimum Viable Completion
- Agent loop runs with webSearch and readPage tools
- Basic fact storage (can be array instead of graph)
- Agent stops after fixed iteration count
- Produces text output summarizing findings
Full Completion
- Knowledge graph with nodes and edges
prepareStepinjects graph summarystopWhenuses confidence threshold- Confidence scoring based on source credibility
- Formatted report with citations
- ASCII graph visualization
Excellence (Going Above and Beyond)
- Real search API integration with rate limiting
- Contradiction detection and flagging
queryGraphtool for agent self-reflection- Interactive graph visualization export
- Incremental research (resume from saved state)
- Comprehensive test suite with >80% coverage
This guide was expanded from AI_SDK_LEARNING_PROJECTS.md. For the complete learning path, see the README.