Project 2: Real-Time Document Summarizer with Streaming UI
Deep Dive Learning Guide
Source: AI_SDK_LEARNING_PROJECTS.md Main Programming Language: TypeScript Alternative Languages: JavaScript, Python, Go Difficulty: Level 2: Intermediate (The Developer) Time Estimate: 1 week Prerequisites: React/Next.js basics, TypeScript fundamentals
Learning Objectives
By completing this project, you will master:
- Server-Sent Events (SSE) Architecture - Understand how to implement unidirectional real-time data flow from server to client over HTTP
- AI SDK streamText API - Learn to use the core streaming function that powers ChatGPT-style interfaces
- Async Iterators and AsyncIterableStream - Master JavaScript’s
for await...ofpattern and async generator functions - React State Management with Streams - Implement efficient incremental state updates without causing excessive re-renders
- AbortController and Cancellation Patterns - Build robust cleanup mechanisms for stopping streams mid-flight
- Next.js API Routes for Streaming - Configure server-side streaming with proper headers and response handling
- Error Handling in Streaming Contexts - Implement graceful degradation when streams fail mid-response
Deep Theoretical Foundation
Server-Sent Events (SSE) Protocol
Server-Sent Events is a standard that allows servers to push data to web clients over HTTP. Unlike WebSockets, SSE is unidirectional (server to client only), simpler to implement, and built on standard HTTP.
SSE Message Format:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ SSE MESSAGE STRUCTURE │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ Each message consists of one or more lines: │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ data: Hello, this is the first chunk │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ data: More data in the same message │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ event: customEvent │ │
│ │ data: {"type": "token", "content": "word"} │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ id: 12345 │ │
│ │ data: Message with ID for reconnection │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ retry: 3000 │ │
│ │ data: Client should reconnect after 3 seconds │ │
│ │ │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ IMPORTANT: Each message ends with TWO newlines (\n\n) │
│ Single newlines separate fields within a message │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘

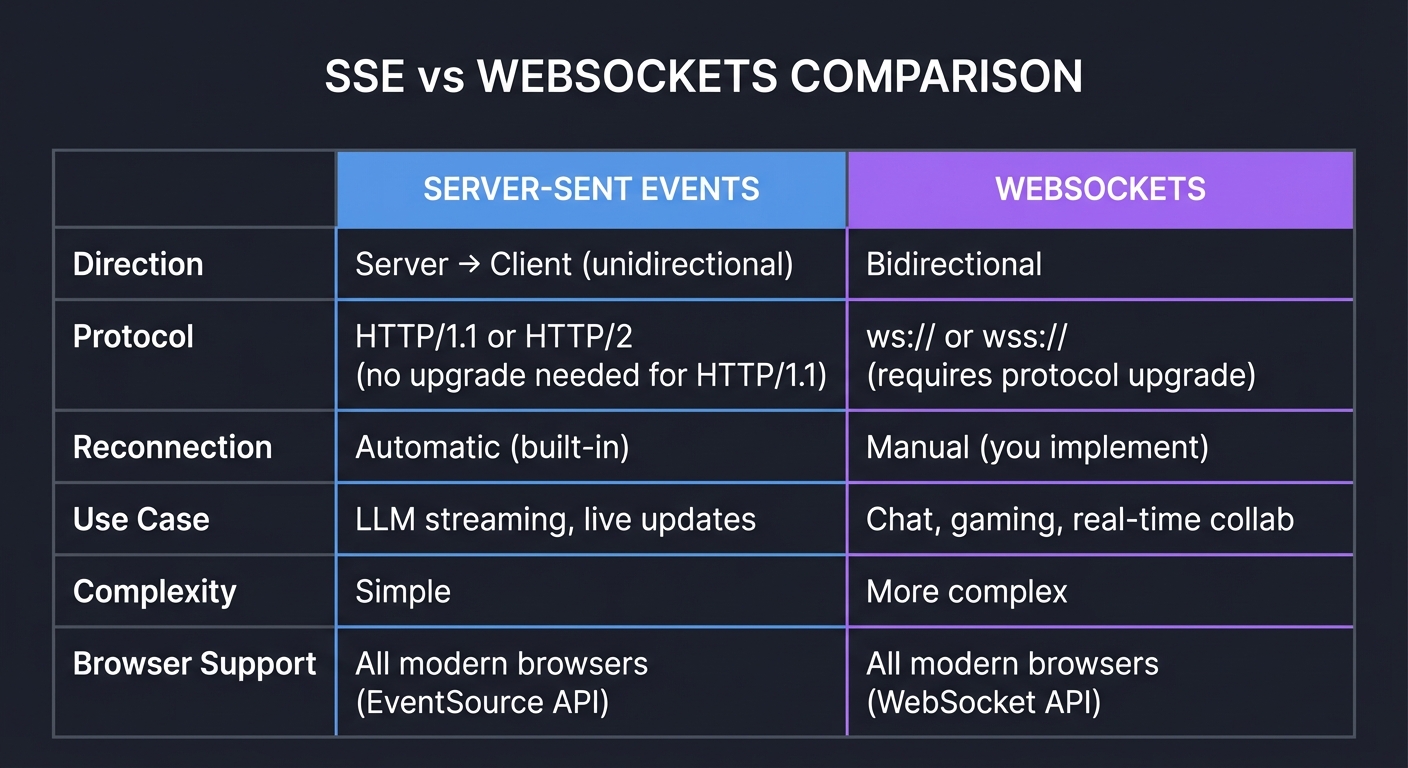
SSE vs WebSockets Comparison:
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ SSE vs WEBSOCKETS COMPARISON │
├────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ SERVER-SENT EVENTS WEBSOCKETS │
│ ────────────────── ────────── │
│ │
│ Direction: Direction: │
│ Server → Client (unidirectional) Bidirectional │
│ │
│ Protocol: Protocol: │
│ HTTP/1.1 or HTTP/2 ws:// or wss:// │
│ (no upgrade needed for HTTP/1.1) (requires protocol upgrade) │
│ │
│ Reconnection: Reconnection: │
│ Automatic (built-in) Manual (you implement) │
│ │
│ Use Case: Use Case: │
│ LLM streaming, live updates Chat, gaming, real-time collab │
│ │
│ Complexity: Complexity: │
│ Simple More complex │
│ │
│ Browser Support: Browser Support: │
│ All modern browsers All modern browsers │
│ (EventSource API) (WebSocket API) │
│ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Why SSE for LLM Streaming:
LLM responses are inherently unidirectional - the user sends a prompt once, then receives a stream of tokens. SSE is perfectly suited because:
- No bidirectional channel needed after the initial request
- Automatic reconnection handles network hiccups
- Works through HTTP proxies without special configuration
- Simpler server implementation (just formatted text output)
Reference: “JavaScript: The Definitive Guide” by David Flanagan - Ch. 15.11 (Server-Sent Events)
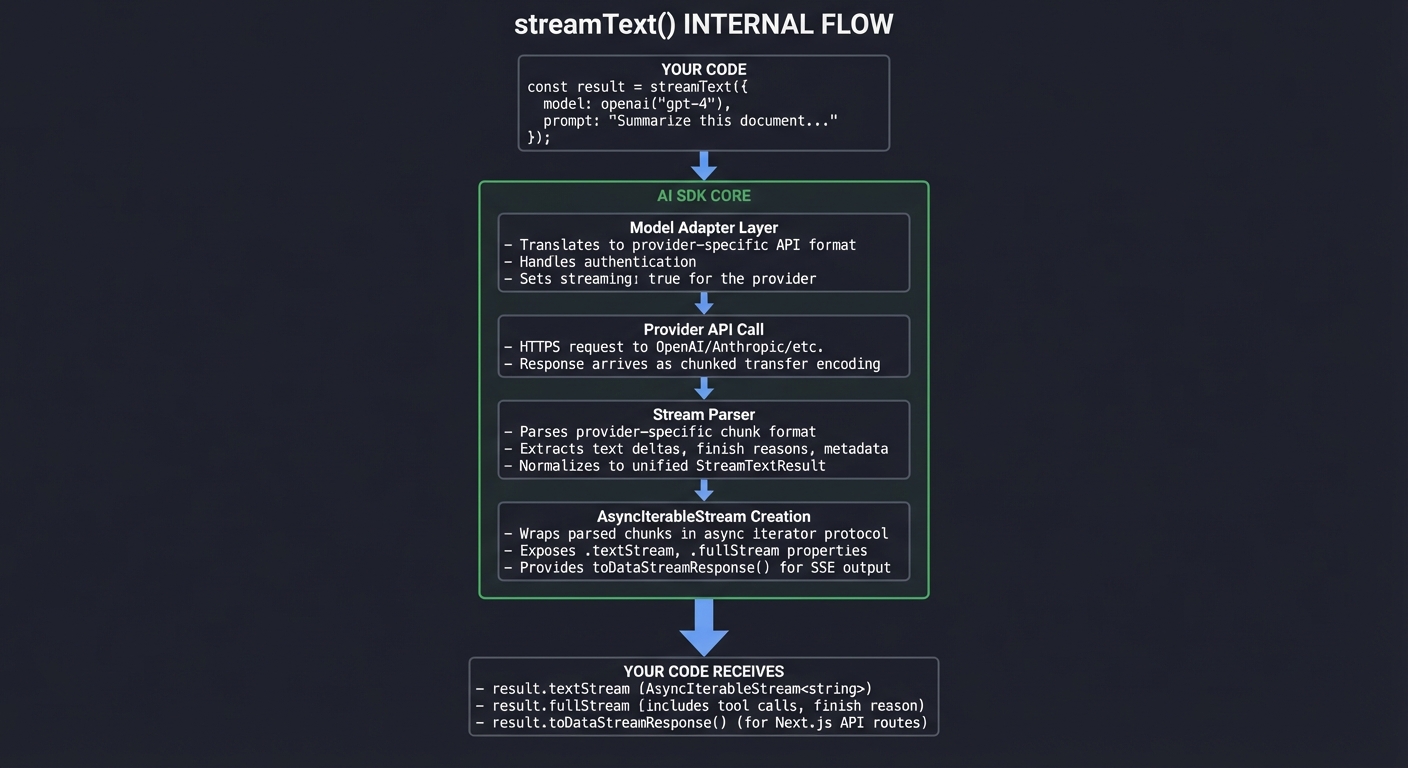
How streamText Works Internally
The AI SDK’s streamText function is the core abstraction that converts LLM API responses into a consumable stream.
Internal Architecture:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ streamText() INTERNAL FLOW │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ YOUR CODE │
│ │ │
│ │ const result = streamText({ │
│ │ model: openai('gpt-4'), │
│ │ prompt: "Summarize this document..." │
│ │ }); │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ AI SDK Core │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ 1. Model Adapter Layer │ │ │
│ │ │ - Translates to provider-specific API format │ │ │
│ │ │ - Handles authentication │ │ │
│ │ │ - Sets streaming: true for the provider │ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ ▼ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ 2. Provider API Call │ │ │
│ │ │ - HTTPS request to OpenAI/Anthropic/etc. │ │ │
│ │ │ - Response arrives as chunked transfer encoding │ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ ▼ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ 3. Stream Parser │ │ │
│ │ │ - Parses provider-specific chunk format │ │ │
│ │ │ - Extracts text deltas, finish reasons, metadata │ │ │
│ │ │ - Normalizes to unified StreamTextResult │ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ ▼ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ 4. AsyncIterableStream Creation │ │ │
│ │ │ - Wraps parsed chunks in async iterator protocol │ │ │
│ │ │ - Exposes .textStream, .fullStream properties │ │ │
│ │ │ - Provides toDataStreamResponse() for SSE output │ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ YOUR CODE RECEIVES: │
│ - result.textStream (AsyncIterableStream<string>) │
│ - result.fullStream (includes tool calls, finish reason) │
│ - result.toDataStreamResponse() (for Next.js API routes) │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Key Properties of streamText Result:
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4'),
prompt: 'Summarize...'
});
// Different stream access patterns:
result.textStream // AsyncIterableStream of just text
result.fullStream // Includes all events (text, tool calls, finish)
result.toDataStreamResponse() // Converts to SSE Response for Next.js
result.toTextStreamResponse() // Plain text stream (simpler, no metadata)
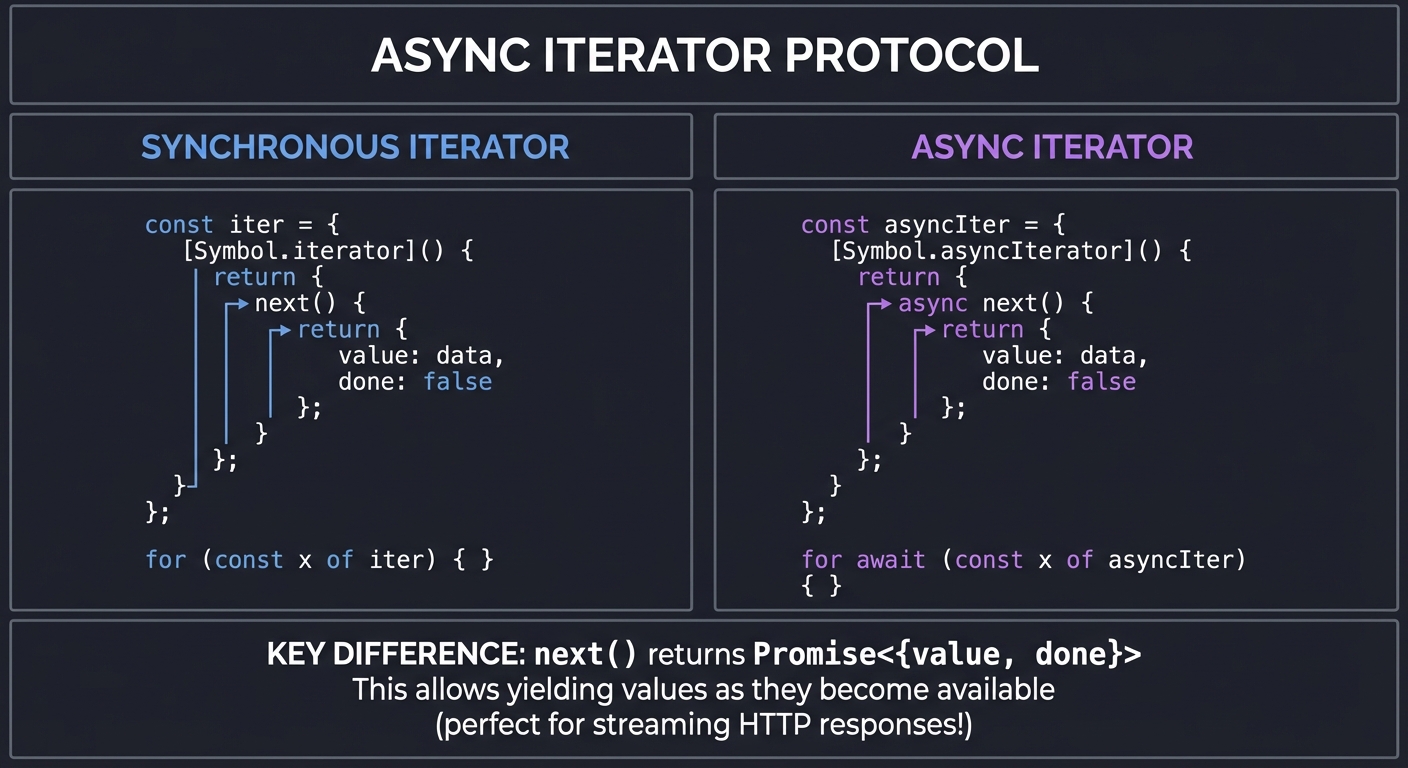
AsyncIterableStream and Async Iterators in JavaScript
Understanding async iterators is crucial for working with streams. The for await...of syntax is how you consume streaming data in JavaScript.
The Async Iterator Protocol:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ASYNC ITERATOR PROTOCOL │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ SYNCHRONOUS ITERATOR ASYNC ITERATOR │
│ ──────────────────── ────────────── │
│ │
│ const iter = { const asyncIter = { │
│ [Symbol.iterator]() { [Symbol.asyncIterator]() { │
│ return { return { │
│ next() { async next() { │
│ return { return { │
│ value: data, value: data, │
│ done: false done: false │
│ }; }; │
│ } } │
│ }; }; │
│ } } │
│ }; }; │
│ │
│ for (const x of iter) { } for await (const x of asyncIter) │
│ { } │
│ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ KEY DIFFERENCE: next() returns Promise<{value, done}> │
│ │
│ This allows yielding values as they become available │
│ (perfect for streaming HTTP responses!) │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Consuming the Stream:
// Method 1: for await...of (most common)
for await (const chunk of result.textStream) {
console.log(chunk); // Each token/word as it arrives
}
// Method 2: Manual iteration
const reader = result.textStream[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
let chunk = await reader.next();
while (!chunk.done) {
console.log(chunk.value);
chunk = await reader.next();
}
// Method 3: Collect all (loses streaming benefit)
const fullText = await result.text; // Waits for completion
Reference: “JavaScript: The Definitive Guide” by David Flanagan - Ch. 13 (Asynchronous JavaScript)
React State Management with Streams
Updating React state during streaming requires careful consideration to avoid performance issues.
The Challenge:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ STREAM STATE UPDATE CHALLENGE │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ NAIVE APPROACH (PROBLEMATIC): │
│ │
│ for await (const chunk of stream) { │
│ setText(prev => prev + chunk); // Re-render on EVERY chunk! │
│ } │
│ │
│ Token arrives every ~50ms │
│ = 20 re-renders per second │
│ = Janky, unresponsive UI │
│ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ BETTER APPROACHES: │
│ │
│ 1. USE AI SDK HOOKS (Recommended) │
│ const { messages, isLoading } = useChat(); │
│ // Handles batching internally │
│ │
│ 2. BATCHED UPDATES │
│ let buffer = ''; │
│ for await (const chunk of stream) { │
│ buffer += chunk; │
│ if (buffer.length >= 50) { // Batch every 50 chars │
│ setText(prev => prev + buffer); │
│ buffer = ''; │
│ } │
│ } │
│ │
│ 3. useTransition FOR NON-URGENT UPDATES │
│ const [isPending, startTransition] = useTransition(); │
│ startTransition(() => setText(prev => prev + chunk)); │
│ // Allows React to interrupt for more urgent updates │
│ │
│ 4. useDeferredValue FOR DISPLAY │
│ const deferredText = useDeferredValue(text); │
│ // Renders stale value if new value causes jank │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Reference: “Learning React, 2nd Edition” by Eve Porcello - Ch. 8 (Hooks), focusing on useTransition and useDeferredValue
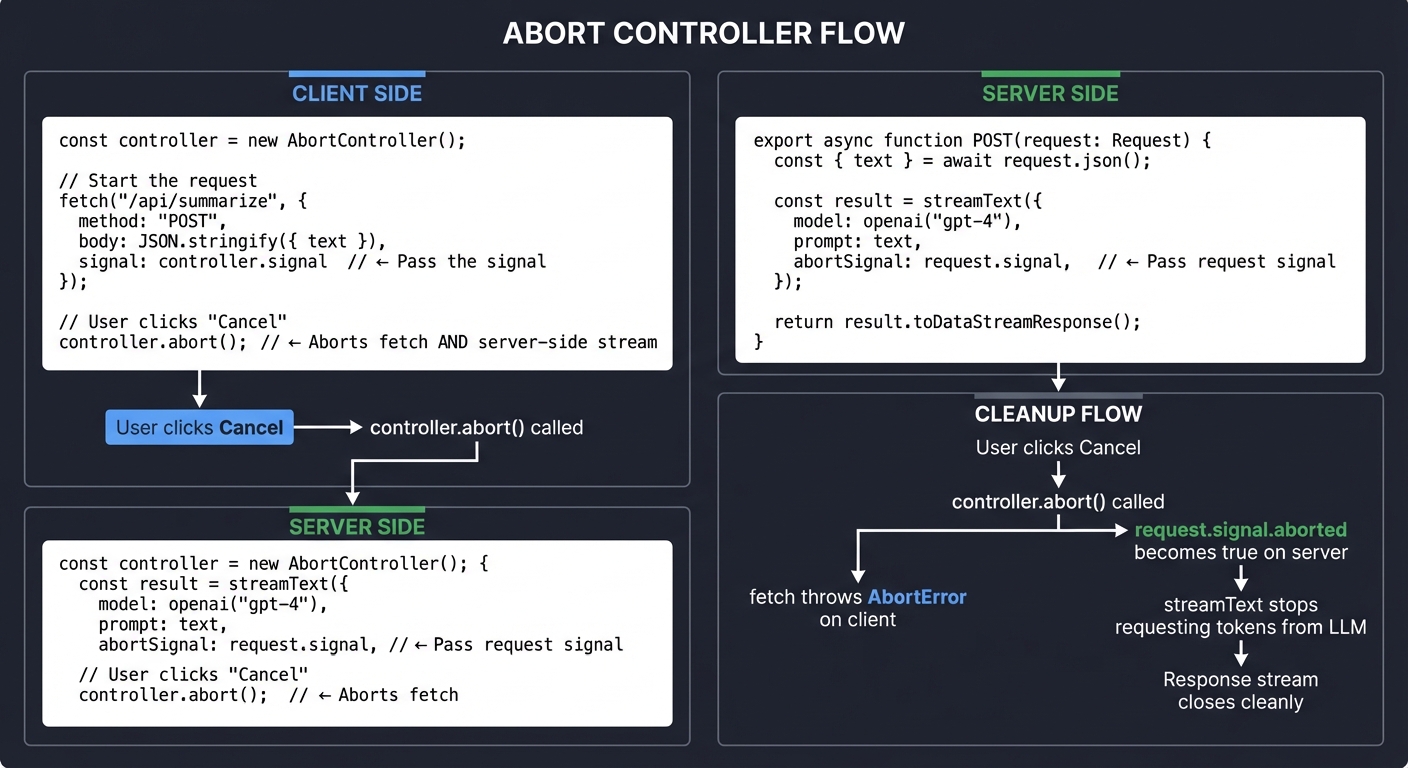
AbortController and Cancellation Patterns
Users need the ability to cancel long-running streams. AbortController is the standard mechanism.
The Cancellation Flow:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ABORT CONTROLLER FLOW │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ CLIENT SIDE: │
│ ───────────── │
│ │
│ const controller = new AbortController(); │
│ │
│ // Start the request │
│ fetch('/api/summarize', { │
│ method: 'POST', │
│ body: JSON.stringify({ text }), │
│ signal: controller.signal // <── Pass the signal │
│ }); │
│ │
│ // User clicks "Cancel" │
│ controller.abort(); // <── Aborts fetch AND server-side stream │
│ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ SERVER SIDE (Next.js API Route): │
│ ───────────────────────────────── │
│ │
│ export async function POST(request: Request) { │
│ const { text } = await request.json(); │
│ │
│ const result = streamText({ │
│ model: openai('gpt-4'), │
│ prompt: text, │
│ abortSignal: request.signal, // <── Pass request's signal │
│ }); │
│ │
│ return result.toDataStreamResponse(); │
│ } │
│ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ CLEANUP FLOW: │
│ │
│ User clicks Cancel │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ controller.abort() called │
│ │ │
│ ├───► fetch throws AbortError on client │
│ │ │
│ └───► request.signal.aborted becomes true on server │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ streamText stops requesting tokens from LLM │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ Response stream closes cleanly │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Cleanup in React Components:
useEffect(() => {
const controller = new AbortController();
fetchAndStream(controller.signal);
return () => {
controller.abort(); // Cleanup on unmount!
};
}, []);
Next.js API Routes for Streaming
Next.js App Router provides native support for streaming responses.
API Route Setup:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ NEXT.JS STREAMING API ROUTE │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ File: app/api/summarize/route.ts │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ import { streamText } from 'ai'; │ │
│ │ import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai'; │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ export async function POST(request: Request) { │ │
│ │ const { document } = await request.json(); │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ const result = streamText({ │ │
│ │ model: openai('gpt-4-turbo'), │ │
│ │ system: 'You are a document summarizer...', │ │
│ │ prompt: `Summarize:\n\n${document}`, │ │
│ │ abortSignal: request.signal, │ │
│ │ }); │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ return result.toDataStreamResponse(); │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ RESPONSE HEADERS (set automatically): │
│ ───────────────────────────────────── │
│ Content-Type: text/event-stream │
│ Cache-Control: no-cache │
│ Connection: keep-alive │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Reference: “Node.js Design Patterns” by Mario Casciaro - Ch. 6 (Streams)
Complete Project Specification
Functional Requirements
- Document Input
- Text area for pasting documents (5,000+ words supported)
- Real-time word count display
- Clear/reset functionality
- Streaming Summary Generation
- Character-by-character display of summary
- Visual cursor indicator during streaming
- Progress indicator (word count of generated summary)
- Estimated time remaining (optional)
- Summary Output Structure
- Key Points (3-5 bullet points)
- Main Themes (2-3 items)
- One-Paragraph Summary
- User Controls
- Summarize button to start generation
- Cancel button during streaming
- Copy to clipboard button
- New document button
- Error Handling
- Display partial results on error
- Show error message with retry option
- Graceful handling of network issues
Non-Functional Requirements
- Performance
- First token visible within 1 second of request
- Smooth 60fps scrolling during streaming
- No visible jank during state updates
- Reliability
- Automatic cleanup on component unmount
- Proper AbortController handling
- Memory leak prevention
- Accessibility
- Screen reader announcements for streaming state
- Keyboard navigation support
- Focus management during state transitions
Real World Outcome
When you open the web app in your browser, here is exactly what you will see and experience:
Initial State:
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Document Summarizer |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| Paste your document here: |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | Paste or type your document text... | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| Document length: 0 words [ Summarize ] |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
After Pasting a Document (5,000+ words):
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Document Summarizer |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| Paste your document here: |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | The field of quantum computing has seen remarkable progress | |
| | over the past decade. Recent breakthroughs in error | |
| | correction, qubit stability, and algorithmic development | |
| | have brought us closer than ever to practical quantum | |
| | advantage. This comprehensive analysis examines... | |
| | [... 5,234 more words ...] | |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| Document length: 5,847 words [ Summarize ] |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
While Streaming (the magic happens!):
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Document Summarizer |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| Summary |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Generating... Progress: 234 words |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | ## Key Points | |
| | | |
| | The article examines recent quantum computing breakthroughs, | |
| | focusing on three critical areas: | |
| | | |
| | 1. **Error Correction**: IBM's new surface code approach | |
| | achieves 99.5% fidelity, a significant improvement over | |
| | previous methods. This breakthrough addresses one of the_ | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| [ Cancel ] |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
The cursor (_) moves in real-time as each token arrives from the LLM. The user watches the summary build word by word - this is the “ChatGPT effect” that makes AI feel alive.
Completed Summary:
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Document Summarizer |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| Summary [Complete] |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Generated in 4.2s Total: 312 words |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | ## Key Points | |
| | | |
| | The article examines recent quantum computing breakthroughs, | |
| | focusing on three critical areas: | |
| | | |
| | 1. **Error Correction**: IBM's new surface code approach | |
| | achieves 99.5% fidelity, a significant improvement... | |
| | | |
| | 2. **Qubit Scaling**: Google's 1,000-qubit processor | |
| | demonstrates exponential progress in hardware capacity... | |
| | | |
| | 3. **Commercial Applications**: First production deployments | |
| | in drug discovery and financial modeling show... | |
| | | |
| | ## Main Themes | |
| | - Race between IBM, Google, and emerging startups | |
| | - Shift from theoretical to practical quantum advantage | |
| | - Growing investment from pharmaceutical and finance sectors | |
| | | |
| | ## One-Paragraph Summary | |
| | Quantum computing is transitioning from experimental to | |
| | practical, with major players achieving key milestones in | |
| | error correction and scaling that enable real-world use cases. | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| [ Copy to Clipboard ] [ Summarize Again ] [ New Doc ] |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
Error State (mid-stream failure):
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Document Summarizer |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| Summary [Error] |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Stopped after 2.1s Partial: 156 words |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | ## Key Points | |
| | | |
| | The article examines recent quantum computing breakthroughs, | |
| | focusing on three critical areas: | |
| | | |
| | 1. **Error Correction**: IBM's new surface code approach | |
| | achieves 99.5% fidelity... | |
| | | |
| | ---------------------------------------------------------------- | |
| | Stream interrupted: Connection timeout | |
| | Showing partial results above. | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| [ Retry ] [ Copy Partial ] [ New Doc ] |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
Key UX behaviors to implement:
- The text area scrolls automatically to keep the cursor visible
- Word count updates in real-time as tokens arrive
- “Cancel” button appears only during streaming
- Partial results are preserved even on error
- Copy button works even during streaming (copies current content)
Solution Architecture
Full Streaming Pipeline
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| COMPLETE STREAMING PIPELINE |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| BROWSER (Client) |
| ---------------- |
| |
| +------------------+ +-------------------+ +----------------+ |
| | DocumentInput | | SummaryDisplay | | ControlBar | |
| | Component |---->| Component |<----| Component | |
| | | | (streaming text) | | (Cancel/Copy) | |
| +------------------+ +-------------------+ +----------------+ |
| | ^ | |
| | | | |
| v | v |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | useSummarize() Hook | |
| | - AbortController management | |
| | - State: text, isLoading, error | |
| | - Fetch with SSE consumption | |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | ^ |
| | POST /api/summarize | SSE stream (text/event-stream) |
| v | |
+-----------+------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| |
| NETWORK (HTTP/1.1) |
| |
+-----------v------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| |
| NEXT.JS SERVER |
| --------------- |
| |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | app/api/summarize/route.ts | |
| | | |
| | export async function POST(request: Request) { | |
| | const { document } = await request.json(); | |
| | | |
| | const result = streamText({ | |
| | model: openai('gpt-4-turbo'), | |
| | prompt: document, | |
| | abortSignal: request.signal, | |
| | }); | |
| | | |
| | return result.toDataStreamResponse(); | |
| | } | |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | ^ |
| | HTTP POST | Chunked response |
| v | |
+-----------+------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| |
| AI SDK CORE |
| |
+-----------v------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| |
| AI SDK |
| ------- |
| |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | streamText() | |
| | | |
| | 1. Translates prompt to OpenAI format | |
| | 2. Sends request with stream: true | |
| | 3. Parses chunked response | |
| | 4. Returns AsyncIterableStream | |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | ^ |
| | | |
| v | |
+-----------+------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| |
| HTTPS |
| |
+-----------v------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| |
| LLM PROVIDER (OpenAI/Anthropic) |
| -------------------------------- |
| |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | GPT-4 / Claude | |
| | | |
| | Generates tokens one at a time | |
| | Returns chunked transfer encoding response | |
| | Each chunk: {"choices":[{"delta":{"content":"token"}}]} | |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Component Breakdown
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| COMPONENT ARCHITECTURE |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| app/ |
| +-- page.tsx # Main page, composes components |
| | |
| +-- components/ |
| | +-- DocumentInput.tsx # Textarea with word count |
| | +-- SummaryDisplay.tsx # Streaming text with cursor |
| | +-- ControlBar.tsx # Summarize/Cancel/Copy buttons |
| | +-- ProgressIndicator.tsx # Word count and time display |
| | +-- ErrorBoundary.tsx # Catch and display errors |
| | |
| +-- hooks/ |
| | +-- useSummarize.ts # Custom hook for streaming logic |
| | |
| +-- api/ |
| +-- summarize/ |
| +-- route.ts # API endpoint with streamText |
| |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Data Flow with SSE Events
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| SSE EVENT DATA FLOW |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| TIME |
| | |
| v CLIENT SERVER LLM |
| | |
| 0ms POST /api/summarize ------> |
| {document: "..."} |
| |
| 50ms Request received |
| streamText() called |
| |
| 100ms <---- token|
| Parse chunk |
| |
| 110ms <------ data: {"text": "The"} |
| setState("The") |
| render() |
| |
| 150ms <---- token|
| Parse chunk |
| |
| 160ms <------ data: {"text": " article"} |
| setState("The article") |
| render() |
| |
| ... (continues for each token) |
| |
| 4200ms <---- done |
| Parse finish |
| |
| 4210ms <------ data: {"finish": "stop"} |
| setIsComplete(true) |
| render() |
| |
| 4220ms Connection closed <------> Response complete |
| |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Recommended File Structure
document-summarizer/
+-- app/
| +-- page.tsx # Main page component
| +-- layout.tsx # Root layout
| +-- globals.css # Global styles
| +-- api/
| +-- summarize/
| +-- route.ts # Streaming API endpoint
|
+-- components/
| +-- document-input.tsx # Text input component
| +-- summary-display.tsx # Streaming text display
| +-- control-bar.tsx # Action buttons
| +-- progress-indicator.tsx # Progress display
| +-- streaming-cursor.tsx # Animated cursor
| +-- error-display.tsx # Error state component
|
+-- hooks/
| +-- use-summarize.ts # Main streaming hook
| +-- use-word-count.ts # Word counting utility
| +-- use-scroll-to-bottom.ts # Auto-scroll behavior
|
+-- lib/
| +-- prompts.ts # System prompts
| +-- utils.ts # Utility functions
|
+-- types/
| +-- index.ts # TypeScript types
|
+-- __tests__/
| +-- hooks/
| | +-- use-summarize.test.ts
| +-- components/
| | +-- summary-display.test.tsx
| +-- api/
| +-- summarize.test.ts
|
+-- package.json
+-- tsconfig.json
+-- next.config.js
+-- .env.local # OPENAI_API_KEY
Phased Implementation Guide
Phase 1: Basic Streaming Setup (Days 1-2)
Milestone: First token renders in the browser from your API route
Tasks:
- Create Next.js project with TypeScript
- Install AI SDK:
npm install ai @ai-sdk/openai - Set up environment variables for OpenAI API key
- Create basic API route at
/api/summarize - Implement minimal
streamTextcall - Create simple page that displays streamed text
Verification:
// Minimal working API route
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const { text } = await request.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4-turbo'),
prompt: `Summarize: ${text}`,
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}
Phase 2: Client-Side Streaming Consumption (Days 3-4)
Milestone: Stream displays character-by-character with state updates
Tasks:
- Create
useSummarizecustom hook - Implement EventSource or fetch with streaming reader
- Handle incremental state updates
- Add loading state management
- Implement basic error handling
Key Code:
// hooks/use-summarize.ts
export function useSummarize() {
const [text, setText] = useState('');
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const summarize = async (document: string) => {
setIsLoading(true);
setText('');
const response = await fetch('/api/summarize', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ document }),
});
const reader = response.body?.getReader();
const decoder = new TextDecoder();
while (reader) {
const { done, value } = await reader.read();
if (done) break;
const chunk = decoder.decode(value);
// Parse SSE format and extract text
setText(prev => prev + extractText(chunk));
}
setIsLoading(false);
};
return { text, isLoading, summarize };
}
Phase 3: Cancellation and Cleanup (Days 4-5)
Milestone: User can cancel mid-stream, no memory leaks on unmount
Tasks:
- Add AbortController to fetch request
- Pass abort signal to API route
- Implement Cancel button in UI
- Add cleanup in useEffect
- Handle AbortError gracefully
Key Code:
const controllerRef = useRef<AbortController | null>(null);
const summarize = async (document: string) => {
// Cancel any existing request
controllerRef.current?.abort();
controllerRef.current = new AbortController();
try {
const response = await fetch('/api/summarize', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ document }),
signal: controllerRef.current.signal,
});
// ... streaming logic
} catch (error) {
if (error.name === 'AbortError') {
// User cancelled - not an error
return;
}
throw error;
}
};
const cancel = () => {
controllerRef.current?.abort();
setIsLoading(false);
};
Phase 4: Polish and UX (Days 5-6)
Milestone: Production-quality UI with all features
Tasks:
- Add animated cursor during streaming
- Implement auto-scroll to keep cursor visible
- Add word count progress indicator
- Implement Copy to Clipboard functionality
- Add proper error display with retry
- Style with Tailwind CSS
Features to Implement:
- Streaming cursor (
_) that appears during generation - Smooth scrolling to bottom of output
- Real-time word count
- Time elapsed display
- Copy button (works during streaming too)
Phase 5: Testing and Optimization (Days 6-7)
Milestone: Tested, optimized, production-ready
Tasks:
- Write unit tests for hooks
- Add integration tests for API route
- Implement React 18 transitions for smooth updates
- Add error boundaries
- Performance optimization
- Accessibility improvements
Testing Strategy
Mocking Streams for Unit Tests
// __tests__/hooks/use-summarize.test.ts
import { renderHook, act } from '@testing-library/react';
import { useSummarize } from '@/hooks/use-summarize';
// Mock streaming response
function createMockStreamResponse(chunks: string[]) {
const encoder = new TextEncoder();
let index = 0;
return new ReadableStream({
pull(controller) {
if (index < chunks.length) {
controller.enqueue(encoder.encode(`data: ${chunks[index]}\n\n`));
index++;
} else {
controller.close();
}
},
});
}
describe('useSummarize', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
global.fetch = jest.fn();
});
it('accumulates streamed text', async () => {
const mockStream = createMockStreamResponse([
'{"text":"Hello"}',
'{"text":" World"}',
]);
(global.fetch as jest.Mock).mockResolvedValue({
ok: true,
body: mockStream,
});
const { result } = renderHook(() => useSummarize());
await act(async () => {
await result.current.summarize('Test document');
});
expect(result.current.text).toBe('Hello World');
});
});
Testing SSE Connections
// __tests__/api/summarize.test.ts
import { POST } from '@/app/api/summarize/route';
describe('/api/summarize', () => {
it('returns SSE content type', async () => {
const request = new Request('http://localhost/api/summarize', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ document: 'Test' }),
});
const response = await POST(request);
expect(response.headers.get('Content-Type'))
.toBe('text/event-stream');
});
it('streams response chunks', async () => {
const request = new Request('http://localhost/api/summarize', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ document: 'Test' }),
});
const response = await POST(request);
const reader = response.body?.getReader();
let receivedChunks = 0;
while (reader) {
const { done, value } = await reader.read();
if (done) break;
receivedChunks++;
}
expect(receivedChunks).toBeGreaterThan(0);
});
});
Testing Cancellation
it('cleans up on abort', async () => {
const controller = new AbortController();
const mockStream = createSlowMockStream();
(global.fetch as jest.Mock).mockResolvedValue({
ok: true,
body: mockStream,
});
const { result } = renderHook(() => useSummarize());
// Start streaming
const promise = act(async () => {
await result.current.summarize('Test');
});
// Cancel mid-stream
act(() => {
result.current.cancel();
});
await promise;
expect(result.current.isLoading).toBe(false);
expect(result.current.text).not.toBe(''); // Partial preserved
});
Common Pitfalls and Debugging
1. Not Closing the Stream Properly
Problem: Memory leaks, hanging connections
// WRONG
const response = await fetch('/api/summarize');
const reader = response.body?.getReader();
// ... but never closing reader
Solution:
// CORRECT
try {
const reader = response.body?.getReader();
// ... process stream
} finally {
reader?.releaseLock();
response.body?.cancel();
}
2. Missing SSE Format in Manual Implementation
Problem: Client doesn’t receive data
// WRONG - Raw text, not SSE format
controller.enqueue(encoder.encode('Hello'));
Solution:
// CORRECT - SSE format with data: prefix and double newline
controller.enqueue(encoder.encode('data: Hello\n\n'));
3. State Updates Causing Excessive Re-renders
Problem: Janky UI during streaming
// WRONG - Re-render on every single token
for await (const chunk of stream) {
setText(prev => prev + chunk);
}
Solution:
// CORRECT - Batch updates
import { startTransition } from 'react';
for await (const chunk of stream) {
startTransition(() => {
setText(prev => prev + chunk);
});
}
4. Forgetting AbortSignal on Server
Problem: LLM keeps generating after client cancels
// WRONG - No abort signal
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4'),
prompt: text,
});
Solution:
// CORRECT - Pass request signal
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4'),
prompt: text,
abortSignal: request.signal,
});
5. Not Handling Partial Results on Error
Problem: User loses all content when stream fails
// WRONG - Clear everything on error
catch (error) {
setText('');
setError(error);
}
Solution:
// CORRECT - Preserve partial results
catch (error) {
// Don't clear text - keep what we received
setError(error);
setIsPartial(true);
}
6. Race Conditions with Multiple Requests
Problem: Old request completes after new one started
// WRONG - No request tracking
const summarize = async (doc) => {
const response = await fetch(...);
for await (const chunk of response) {
setText(prev => prev + chunk); // Which request?
}
};
Solution:
// CORRECT - Track request ID
const requestIdRef = useRef(0);
const summarize = async (doc) => {
const thisRequestId = ++requestIdRef.current;
for await (const chunk of response) {
if (thisRequestId !== requestIdRef.current) return;
setText(prev => prev + chunk);
}
};
7. Missing Error Boundaries
Problem: Uncaught errors crash the entire app
// WRONG - No error boundary
<SummaryDisplay text={text} />
Solution:
// CORRECT - Wrap with error boundary
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<ErrorDisplay />}>
<SummaryDisplay text={text} />
</ErrorBoundary>
Extensions and Challenges
Extension 1: Multiple Summary Formats
Add options for different summary types:
- Executive Summary (1-2 paragraphs)
- Bullet Points Only (5-10 points)
- Academic Abstract (formal style)
- TL;DR (1-2 sentences)
Use streamObject to return structured data:
const result = streamObject({
model: openai('gpt-4-turbo'),
schema: z.object({
keyPoints: z.array(z.string()),
themes: z.array(z.string()),
summary: z.string(),
}),
prompt: document,
});
Extension 2: Document Upload Support
Add file upload for:
- PDF documents (with pdf-parse)
- Word documents (with mammoth)
- Markdown files
- Plain text files
Implement chunking for documents that exceed context limits.
Extension 3: Summary History with Local Storage
Store summaries locally:
- Save summaries with timestamps
- Allow re-viewing past summaries
- Export history as JSON
- Clear individual or all history
Extension 4: Comparison Mode
Summarize two documents and compare:
- Side-by-side streaming display
- Highlight similarities and differences
- Generate comparison summary
Resources
Books with Specific Chapters
| Topic | Book | Chapter/Section |
|---|---|---|
| Async JavaScript & Iterators | “JavaScript: The Definitive Guide” by David Flanagan | Ch. 13 (Asynchronous JavaScript) |
| Server-Sent Events | “JavaScript: The Definitive Guide” by David Flanagan | Ch. 15.11 (Server-Sent Events) |
| React State Management | “Learning React, 2nd Edition” by Eve Porcello | Ch. 8 (Hooks) |
| React Server Integration | “Learning React, 2nd Edition” by Eve Porcello | Ch. 12 (React and Server) |
| Streaming in Node.js | “Node.js Design Patterns, 3rd Edition” by Mario Casciaro | Ch. 6 (Streams) |
| Error Handling Patterns | “Release It!, 2nd Edition” by Michael Nygard | Ch. 5 (Stability Patterns) |
| Web APIs & Fetch | “JavaScript: The Definitive Guide” by David Flanagan | Ch. 15 (Web APIs) |
Recommended Reading Order
- Start with Flanagan Ch. 13 to understand async/await and async iterators
- Read Flanagan Ch. 15.11 for SSE fundamentals
- Move to Porcello Ch. 8 for React hooks patterns
- Then tackle the AI SDK documentation with this foundation
- Read Casciaro Ch. 6 for deeper stream understanding
Online Resources
- MDN Server-Sent Events
- AI SDK streamText Documentation
- AI SDK UI Hooks
- React 18 Working Group: useTransition
- Next.js Streaming Documentation
- Vercel AI SDK Examples Repository
Self-Assessment Checklist
Use these questions to verify your understanding before considering this project complete:
Fundamentals (Must answer all correctly)
- Q1: What is the difference between SSE and WebSockets? When would you use each?
- Q2: What does
for await...ofdo and how is it different from regularfor...of? - Q3: Explain what
Symbol.asyncIteratoris and why it matters for streaming. - Q4: What HTTP headers are required for an SSE response?
- Q5: Why does
toDataStreamResponse()exist? What does it do?
Implementation (Demonstrate by doing)
- Q6: Your stream is working but updates feel janky. What React 18 feature would you use and why?
- Q7: A user navigates away from the page mid-stream. What happens if you don’t implement cleanup?
- Q8: The network drops mid-stream. What data does the user see? How do you handle this gracefully?
- Q9: Two summarization requests are made quickly in succession. What bug might occur and how do you prevent it?
- Q10: How do you test a streaming API route without actually calling the LLM?
Architecture (Explain in your own words)
- Q11: Draw the data flow from user click to rendered text. Include all layers (React, API route, SDK, LLM).
- Q12: Why does the AI SDK parse the LLM response before passing it to you? What format does it come in raw?
- Q13: What is “backpressure” in streaming and does it affect your browser-based client?
- Q14: Explain why SSE is a better choice than polling for LLM responses.
- Q15: What information is in
result.fullStreamthat isn’t inresult.textStream?
Debugging Scenarios (How would you fix?)
- Q16: Your API returns 200 but the browser shows no text. What’s likely wrong?
- Q17: Cancellation works on the client but the LLM keeps generating (you see charges). What did you forget?
- Q18: The summary appears all at once at the end instead of streaming. What’s wrong with your client code?
The Core Question This Project Answers
“How do I stream LLM responses in real-time to create responsive, interactive UIs?”
This is about understanding the entire streaming pipeline from the AI SDK’s async iterators through Server-Sent Events to React state updates. You’re not just calling an API - you’re building a real-time data flow that makes AI feel alive and responsive.
When you can explain every layer of this pipeline and handle edge cases gracefully, you’ve mastered one of the most important patterns in modern AI application development.
Next Project: P03 - Code Review Agent with Tool Calling