Learn ARM: From Zero to ARM Architecture Master - Expanded Project Guides
Generated from:
LEARN_ARM_DEEP_DIVE.md
Overview
ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) is the most widely used processor architecture in the world, powering over 200 billion devices. From your iPhone to your smart thermostat, from data center servers to the Nintendo Switch—ARM is everywhere. This learning path takes you from understanding basic ARM instruction encoding to building complete operating systems and game consoles on bare metal.
After completing these projects, you will:
- Understand every register and their purposes
- Read and write ARM assembly fluently
- Know how instructions flow through the pipeline
- Build bare-metal systems without an operating system
- Create bootloaders, drivers, and schedulers
- Understand the difference between ARM32, Thumb, and AArch64
- Debug ARM binaries like a professional reverse engineer
Project Index
| # | Project | Difficulty | Time | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ARM Instruction Decoder & Disassembler | Intermediate | 1-2 weeks | ISA encoding, binary parsing |
| 2 | ARM Assembly Calculator | Beginner | Weekend | Registers, syscalls, basic assembly |
| 3 | Bare-Metal LED Blinker | Advanced | 1-2 weeks | Boot sequence, GPIO, linker scripts |
| 4 | UART Driver from Scratch | Advanced | 1-2 weeks | Serial I/O, interrupts, ring buffers |
| 5 | ARM Memory Allocator | Advanced | 1-2 weeks | Heap management, alignment, coalescing |
| 6 | Simple Bootloader | Expert | 2-4 weeks | Flash programming, XMODEM, firmware updates |
| 7 | Context Switcher & Mini-Scheduler | Expert | 2-4 weeks | Multitasking, SysTick, TCBs |
| 8 | ARM Emulator | Master | 1 month+ | Complete ISA emulation, CPU simulation |
| 9 | Exception Handler & Fault Analyzer | Expert | 1-2 weeks | CFSR, stack traces, fault recovery |
| 10 | I2C Driver for OLED Display | Advanced | 1-2 weeks | I2C protocol, SSD1306, graphics |
| 11 | SPI Driver for SD Card | Advanced | 2-3 weeks | SPI protocol, FAT filesystem |
| 12 | Timer-Based PWM Motor Controller | Intermediate | 1 week | Timers, PWM, encoders |
| 13 | DMA-Driven Audio Player | Expert | 2-3 weeks | DMA, DAC, double buffering |
| 14 | ARM Debugger (GDB Stub) | Master | 1 month+ | Debug architecture, breakpoints, RSP |
| 15 | Tiny Operating System | Master | 1-2 months | MPU, syscalls, IPC, scheduling |
| 16 | Capstone: ARM Game Console | Master | 2-3 months | Complete system integration |
Learning Paths
If you’re completely new to ARM:
- Project 2: Assembly Calculator - Get comfortable with ARM assembly syntax
- Project 1: Instruction Decoder - Understand how instructions are encoded
- Project 3: Bare-Metal LED - Your first real hardware project
If you have some embedded experience:
- Project 3: Bare-Metal LED - Verify your bare-metal skills
- Project 4: UART Driver - Build your debug console
- Project 10: I2C OLED - Visual feedback is motivating!
- Project 7: Context Switcher - Core RTOS concept
If you want deep understanding:
- Projects 1-3 (foundations)
- Projects 4-5 (peripherals and memory)
- Projects 6-7 (boot and multitasking)
- Project 8: ARM Emulator - The ultimate learning project
- Project 15: Tiny OS - Put it all together
Prerequisites
Essential Knowledge
- C programming fundamentals (pointers, bitwise operations, structs)
- Understanding of binary and hexadecimal number systems
- Basic understanding of what assembly language is
- Familiarity with command line tools
Helpful but Not Required
- Previous embedded systems experience
- x86 assembly knowledge (transfers somewhat)
- RTOS experience (FreeRTOS, etc.)
- Electronics basics (for hardware projects)
Hardware Requirements
Minimum kit (~$25):
- STM32 Nucleo-F411RE or Nucleo-F446RE board
- USB cable (included)
- Breadboard and jumper wires
Recommended additions (~$50 more):
- SSD1306 OLED display (I2C)
- MicroSD card module
- Small speaker/buzzer
- DC motor with L298N driver
- Rotary encoder
Core Concepts Overview
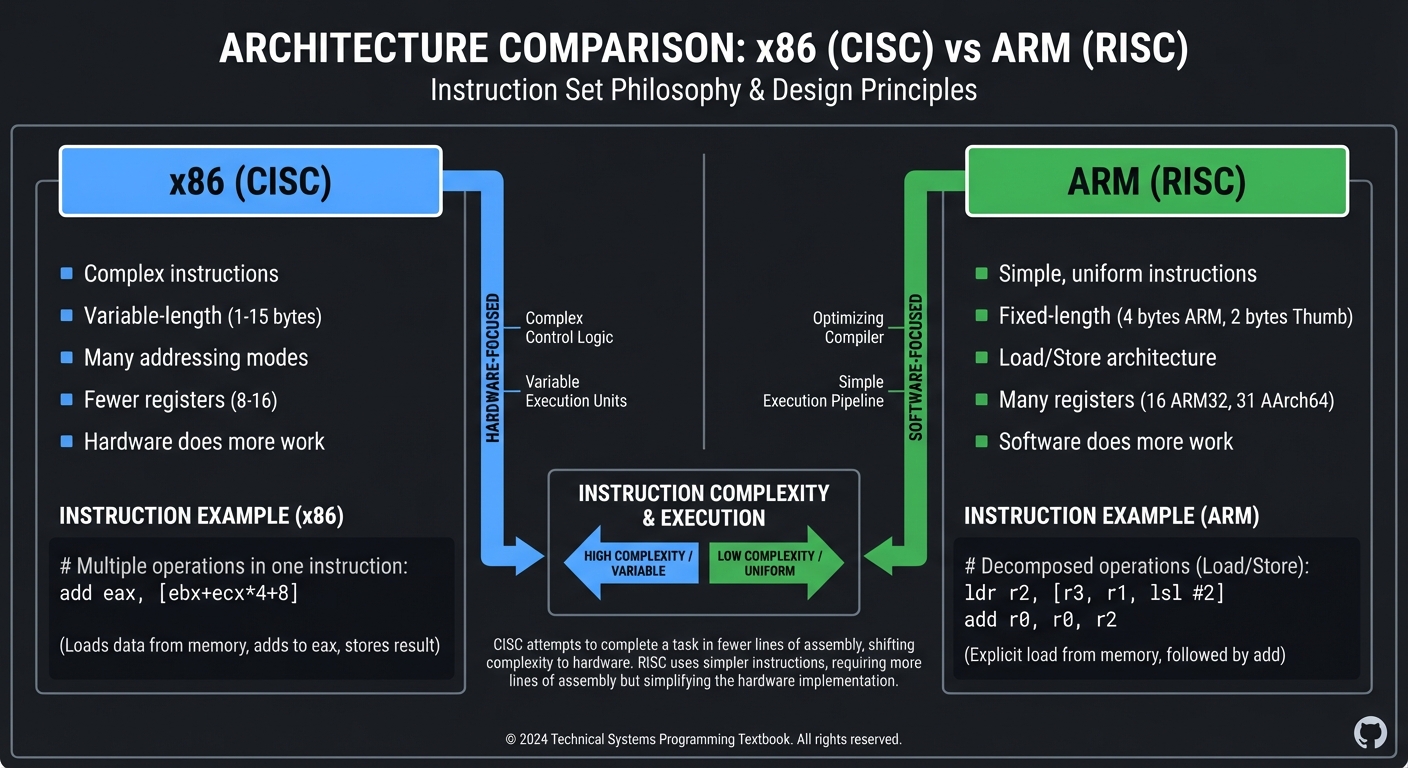
ARM vs x86 Philosophy
x86 (CISC): ARM (RISC):
├── Complex instructions ├── Simple, uniform instructions
├── Variable-length (1-15 bytes) ├── Fixed-length (4 bytes ARM, 2 bytes Thumb)
├── Many addressing modes ├── Load/Store architecture
├── Fewer registers (8-16) ├── Many registers (16 ARM32, 31 AArch64)
└── Hardware does more work └── Software does more work
Fundamental Concepts Mastered Through These Projects
- Load/Store Architecture - Projects 1-3
- Conditional Execution - Projects 1-2, 8
- Barrel Shifter - Projects 1, 8
- Instruction Pipelining - Projects 1, 8
- Processor Modes - Projects 6-7, 9, 15
- Exception Handling - Projects 6-7, 9, 14-15
- Memory Management - Projects 5, 15
Essential Resources
Books (Priority Order)
- “The Art of ARM Assembly, Volume 1” by Randall Hyde
- “The Definitive Guide to ARM Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4” by Joseph Yiu
- “Making Embedded Systems, 2nd Edition” by Elecia White
- “Computer Organization and Design ARM Edition” by Patterson & Hennessy
- “Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces” by Arpaci-Dusseau
Online Tutorials
Official Documentation
Remember: ARM is learned by doing, not just reading. Pick a project that excites you, get the hardware, and start building. Every bug you fix teaches you something new about how ARM really works.